Fix Cloud Functions Deployment
- You must have a Firebase project connected to FlutterFlow.
- Ensure your project is on the Blaze Plan.
Cloud Functions allow you to execute backend code in response to events triggered by Firebase features or HTTPS requests. Various situations might cause Cloud Functions to malfunction, often stemming from setup problems or coding mistakes within the Cloud Function's script.
This article guides you through common challenges with Cloud Functions in FlutterFlow and how to resolve them.
Errors Shown in FlutterFlow Builder
You may encounter the following errors in the FlutterFlow Builder:
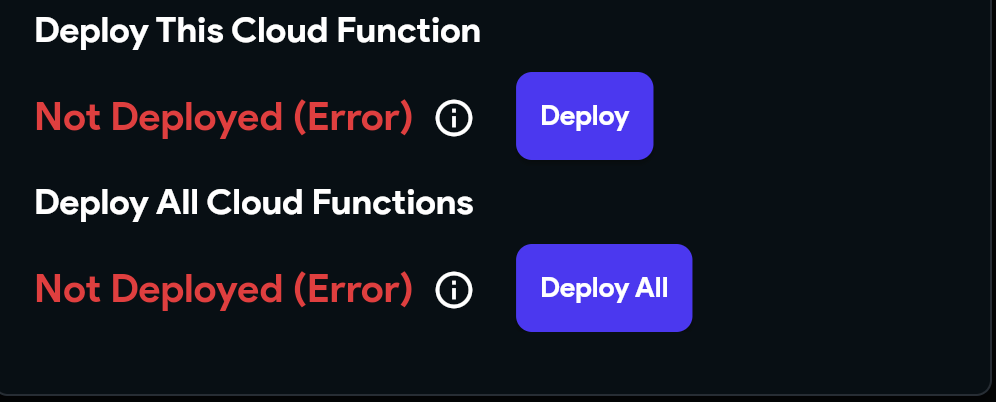
Out of Date (Error)Not Deployed (Error)
These errors can arise from various situations. Below are screenshots of these errors:
Out of Date Error

Not Deployed Error
Key Checks for Resolving Deployment Errors
-
Verify firebase@flutterflow.io Has Necessary Permissions
To ensure FlutterFlow works smoothly with your project, ensure that
firebase@flutterflow.iohas the following permissions in your Firebase project:- Cloud Functions Admin
- Editor
- Service Account User
Follow the steps below to add these permissions:
-
Go to the Firebase Console and log into your account.
-
Open your project and go to Project Settings > Users and Permissions.
-
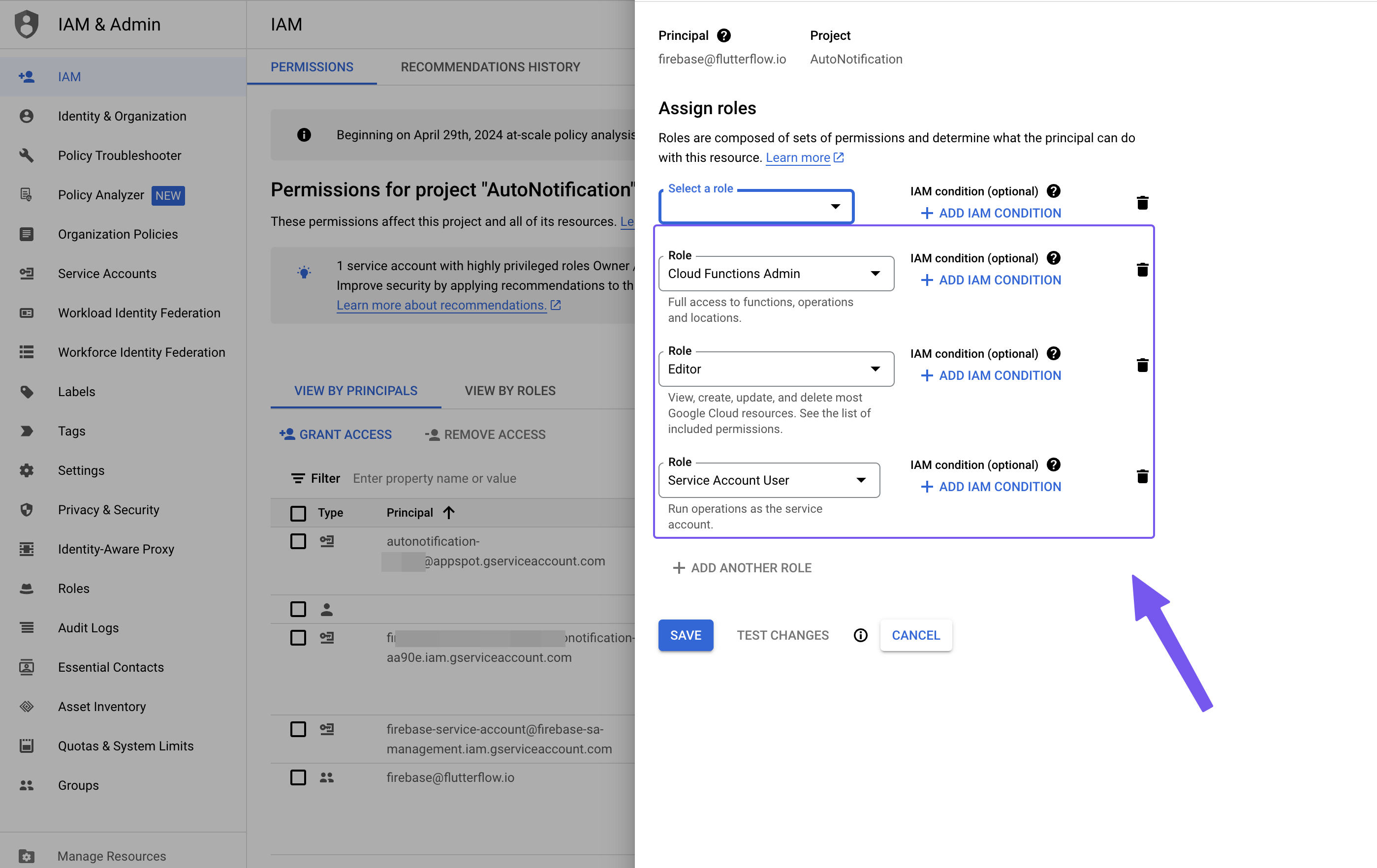
Under Advanced Settings Permissions, locate
firebase@flutterflow.io, click Edit, and add the required roles.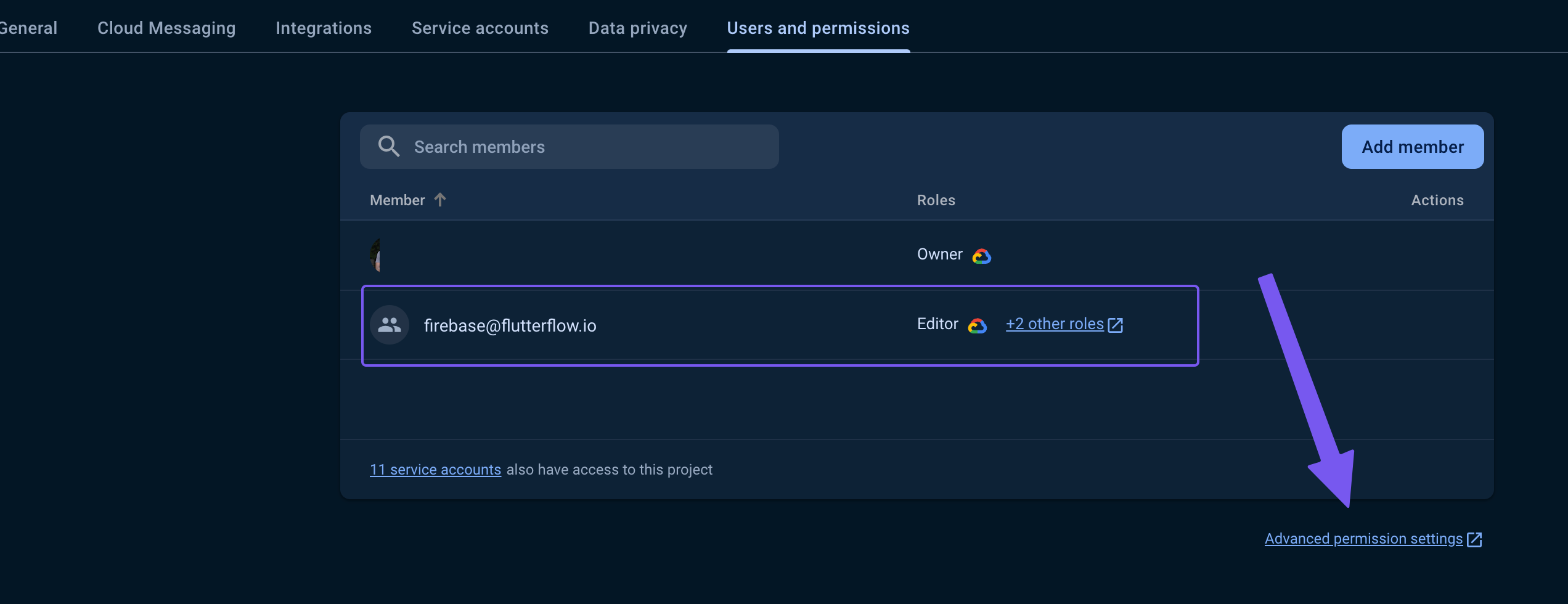
-
Check for Function Name Mismatch
Ensure the function name in your code exactly matches the function name defined in FlutterFlow.
For example, in this case, FlutterFlow expects
logoMaker, but the code incorrectly usesdata.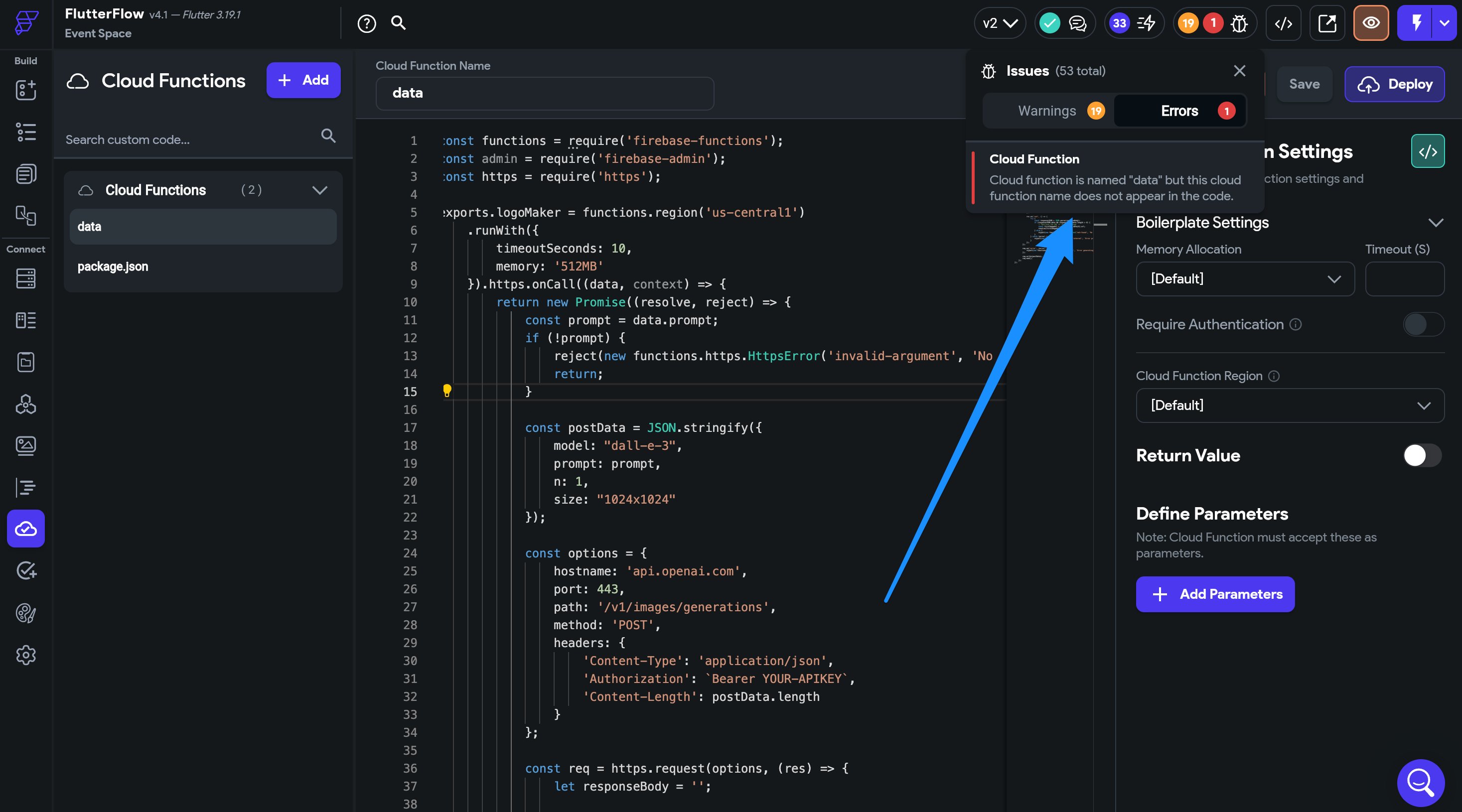
-
Validate Custom Code for Cloud Functions
Small mistakes in your custom Cloud Functions code can prevent deployment.
-
Double-check your code for errors.
-
Test locally using an IDE or Firebase CLI.
-
-
Verify Firebase Billing Plan (Blaze Plan Required):
- Ensure your Firebase project is on the Blaze Plan, not Spark Plan.
- Check billing status on GCP. Even if Firebase shows Blaze, GCP billing issues may still block deployments.
-
Check if Other Cloud Functions Are Deploying:
- If some Cloud Functions (like Push Notification or Stripe) are deploying successfully, it indicates your Firebase setup is mostly correct.
- Focus on inspecting your specific function code and configuration.
-
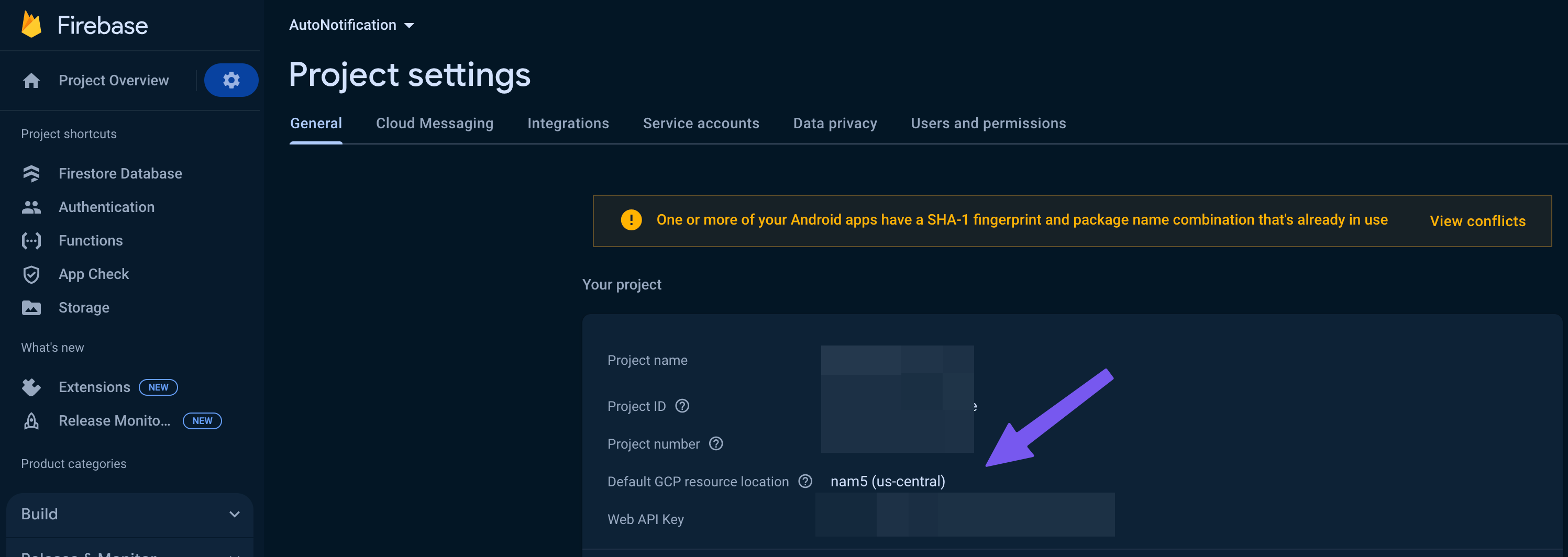
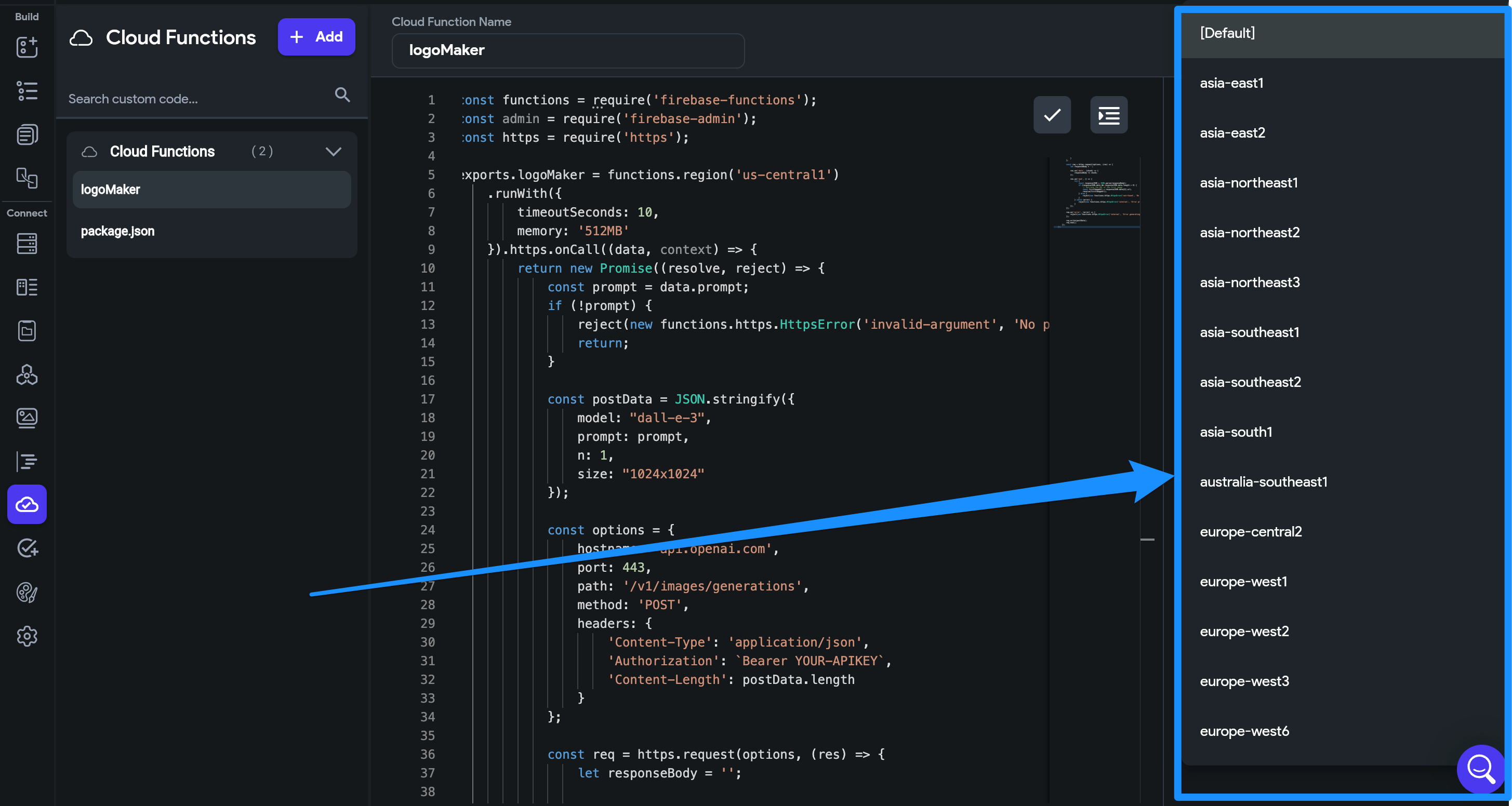
Ensure Region Selection Matches Firebase Project:
-
The region set for your Cloud Function in FlutterFlow should match your Firebase project's region.
-
Do not leave the region as
[default].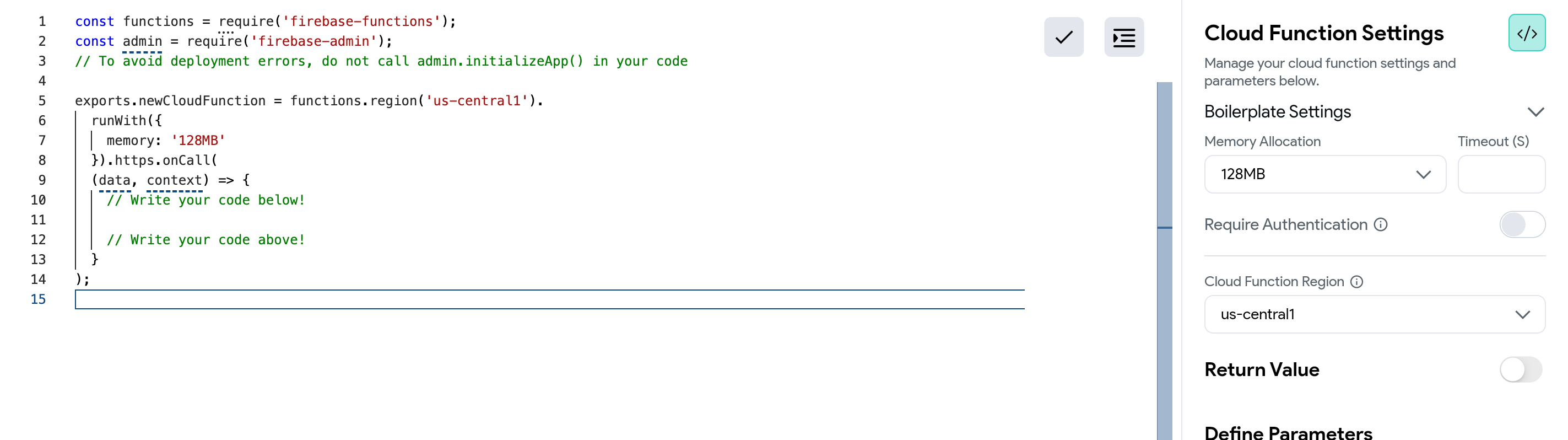
tipIf you previously deployed functions in the wrong region, delete them, set the correct region, and re-deploy.
-
-
Protocol Conflicts: HTTP vs Callable Functions
If you initially deployed a function as HTTP and later try to redeploy it as Callable (or vice versa), you'll get this error:
[makeUserAdmin(us-central1)] Changing from an HTTPS function to a callable function is not allowed. Please delete your function and create a new one instead.Follow the steps below to fix this error:
- Delete the existing function in Firebase Console.
- Modify the protocol type in FlutterFlow.
- Redeploy the function.
-
Verify
package.jsonIntegrity-
Use the generated
package.jsonfile as-is unless you need to add extra packages. -
Ensure it’s not blank and doesn’t contain invalid characters.
Recommended structure:
{
"name": "functions",
"description": "Firebase Custom Cloud Functions",
"engines": {
"node": "18"
},
"main": "index.js",
"dependencies": {
"firebase-admin": "^11.8.0",
"firebase-functions": "^4.3.1"
},
"private": true
}
-
-
Ensure Packages Are Included in
package.jsonIf you are using third-party packages (e.g.,
axios), make sure they are properly added to thedependenciessection inpackage.json: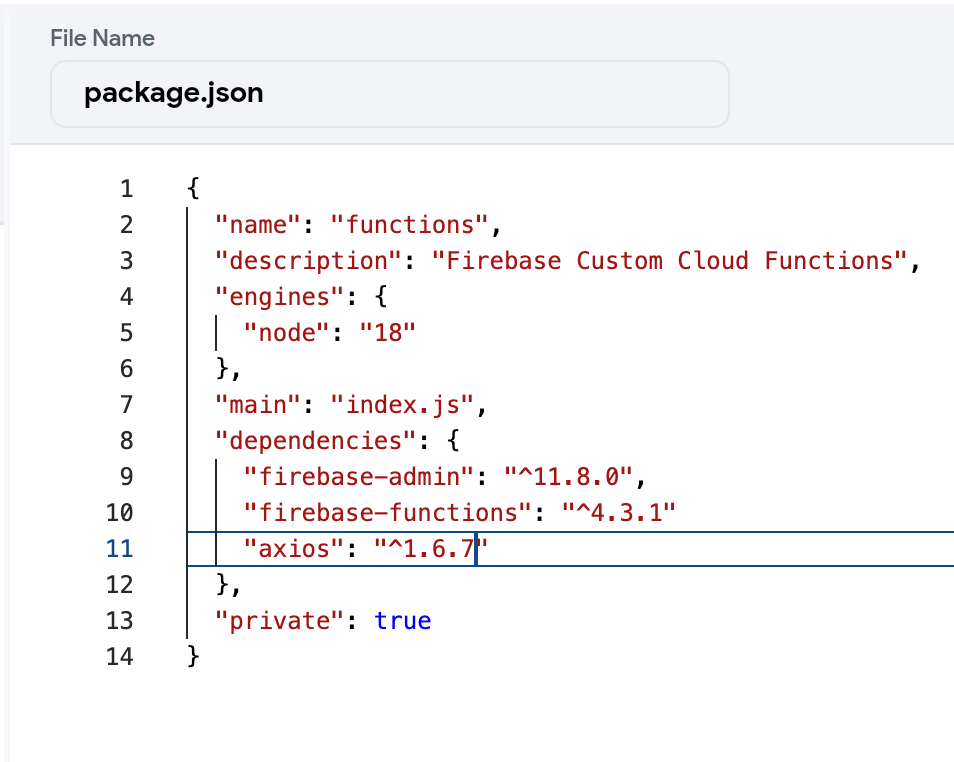
-
Validate Third-Party Package Versions
The versions specified in your
package.jsonshould match available versions listed on npmjs.com.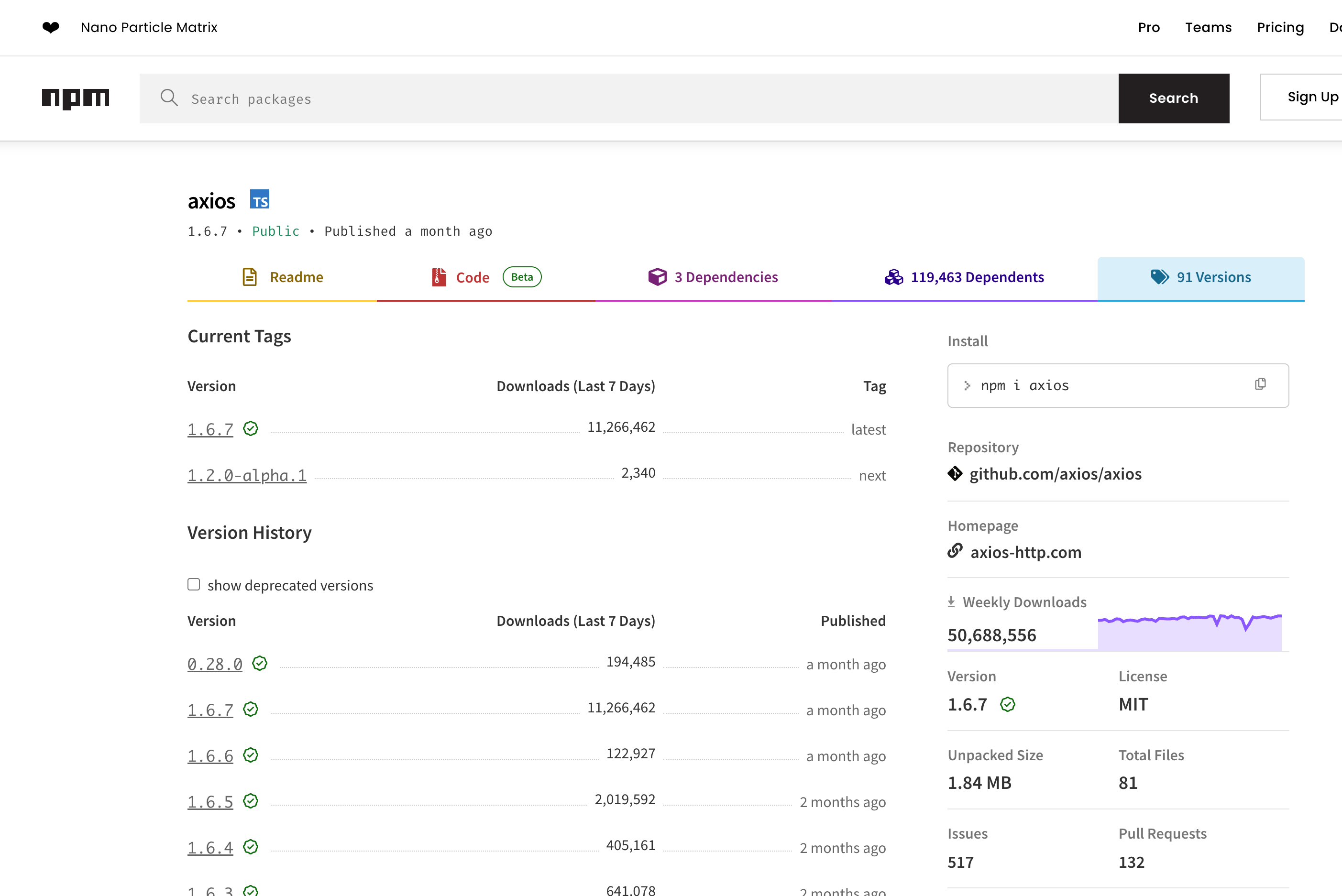
-
Check for Undeployed Firebase Rules and Indexes:
- Incomplete Firestore rules or indexes can block function deployment.
- Make sure all rules and indexes have been deployed from FlutterFlow.
Additional Troubleshooting and Optimization:
-
Trigger Configuration Issues
If your Cloud Functions are not being triggered:
Review Event Triggers:
- For Firestore triggers: verify document paths and collection names.
- For HTTP functions: ensure correct setup in FlutterFlow.
Check Permissions and Rules:
- Firebase security rules and project permissions must allow the Cloud Function operations.
-
Execution Timeouts
-
Cloud Functions may fail if execution time exceeds limits.
-
Set a custom timeout duration in FlutterFlow:
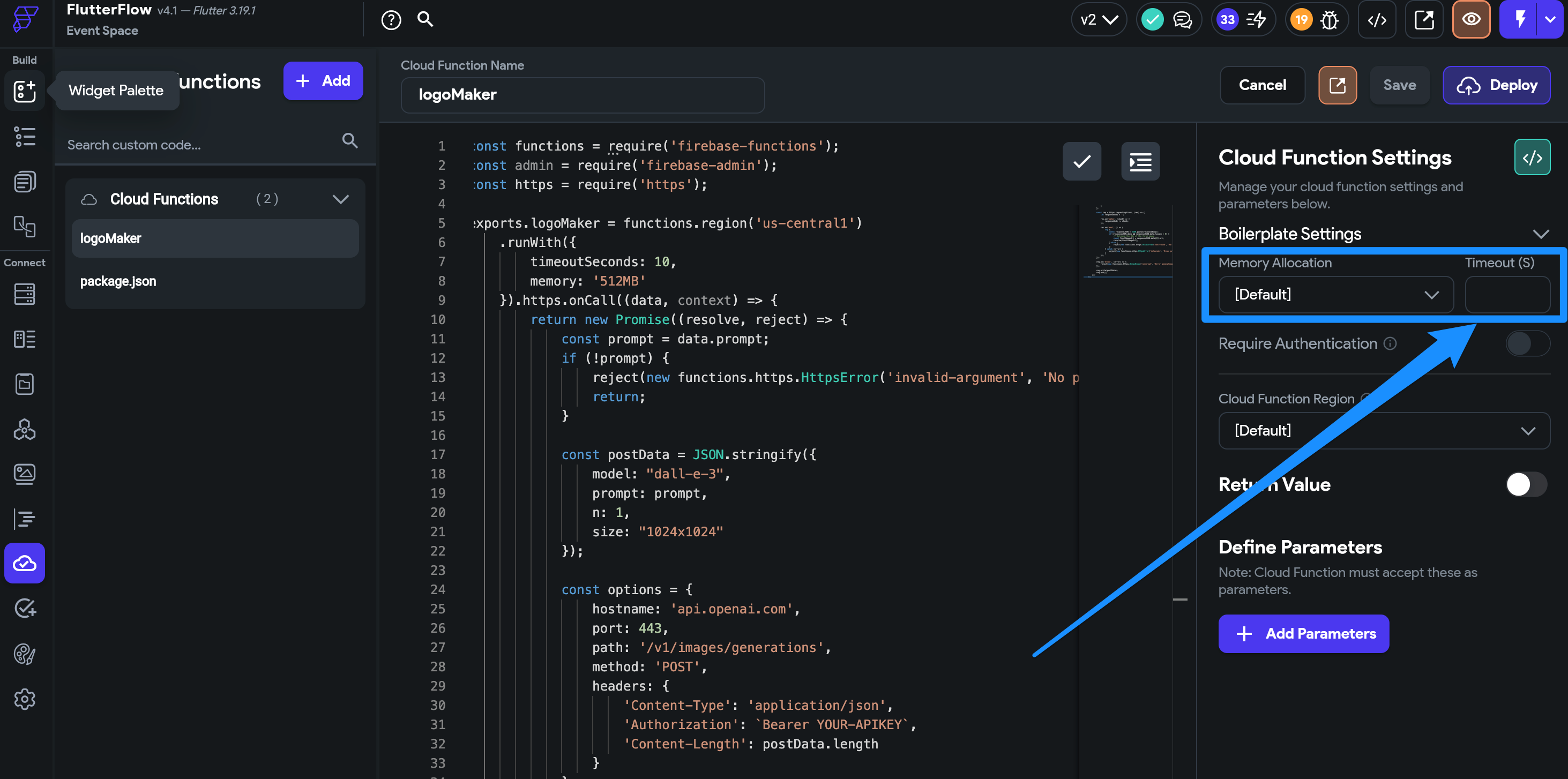
For longer processing tasks, increase the timeout duration in your Cloud Function configuration.
Configuring Cloud Function regions in FlutterFlow can also optimize performance:
 note
noteLonger timeouts may increase Firebase costs.
-
-
Cold Start Delays
Cloud Functions may respond slower after periods of inactivity:
- Use Cloud Scheduler to periodically invoke functions and keep them warm.
- Minimize dependencies to reduce cold start delays.
Following this comprehensive troubleshooting guide should help you resolve most issues encountered when working with Cloud Functions.