FlutterFlow State Management
This document explains the generated code behind the state management approaches used in FlutterFlow. If you're looking for guidance on adding state variables in FlutterFlow, refer to the State Variables documentation.
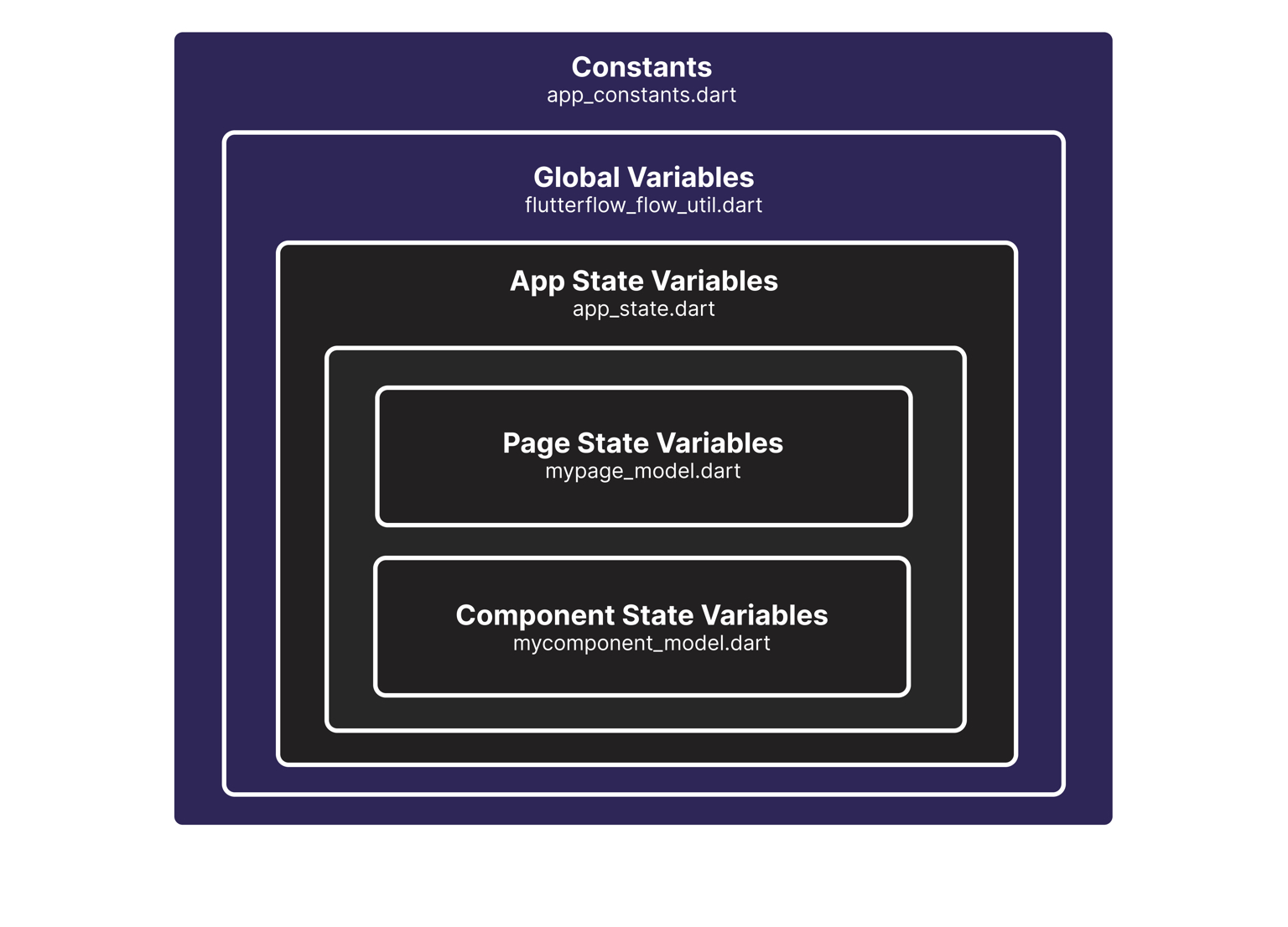
FlutterFlow manages state in several ways, depending on the scope.
Generally, state management is handled using the Provider package, which facilitates the provisioning of data models for components, pages, and the overall app state.
Page & Component Models
In FlutterFlow, both component widget models and page models share a uniform structure, enhancing consistency throughout the framework. They include local state fields to store data specific to the component, such as sizes or user inputs. These models are also equipped with initialization and disposal methods: initState for setup when the widget initializes, and dispose for resource cleanup when the widget is no longer needed.
Additionally, they provide space for action blocks, which are a set of actions that performs a specific task and can be reused in different parts of the app, and helper methods for extra functionalities needed by the component. This consistent structure across models helps efficiently manage the state and interactions of various components within the app.
Page State
Variables used exclusively within a page — such as a text field validator or the value of a checkbox — are stored in the Model of each page. These variables can be accessed by other component children on the same page. For instance, on a page with a form, tapping a button in one component may need to access the value of a text field in a different component.
Variables within a page are tracked through StatefulWidget and are encapsulated into that page’s Model.
Component State
Similar to page state, Component State variables are accessible within the component where they are defined. Each component has a corresponding Model and Widget class. Variables may be passed in from their parent as parameters. Additionally, you can access component state values from its parent Page widget.
This accessibility is possible because the Model of a component is instantiated within the parent Page model. It utilizes the Provider method context.read(), which returns any existing model in the tree before instantiating a new one. Thus, any updates to the state in the component model will reflect in the parent’s instance of that component model.
One of the helper methods in flutter_flow_model.dart is wrapWithModel(). This method wraps the child in a Provider model to make it accessible to the child and sets a callback function, which is generally used to call setState() in the parent page and update any changed values. We use this wrapper around widgets that need to access the data included in the model.
For example, if a page includes a component with a text field and later on the page there is a button needing access to the text field’s value, the button would be wrapped with wrapWithModel(), including the text field component’s Model as a parameter.
It’s important to note that components cannot directly access variables of other components on the same page. However, you can pass a variable from ComponentA as a parameter to ComponentB in their parent Page. This ensures that ComponentB receives all updates from ComponentA as expected.
App State
The generated code behind FlutterFlow's App State class is explained in the FFAppState documentation.
Variables
Variables required across multiple pages of the app, such as a username, should be added to the App State. Refer to lib/app_state.dart.
All defined variables within the app state are components of the FFAppState class, which functions as a ChangeNotifier. This means listeners can subscribe and receive notifications when any changes occur.
On each page that requires access to app state variables, the method context.watch<AppState>() is called to initialize a listener for that page. This watch() method, provided by the Provider package, facilitates access to inherited widgets and acts as an effective wrapper.
Persisting App State
When an app state variable is created, selecting the "Persisted" option enables FlutterFlow to save it on the device using the Shared Preferences package. This ensures the variable remains available even after the app is restarted, making it ideal for persisting settings such as login status or a user's choice between light and dark modes.
If the "Secure Persisted Fields" option is enabled in the app state settings, FlutterFlow utilizes the Flutter Secure Storage package to encrypt the data.
If the platform is Android, then flutter_secure_storage stores data in encryptedSharedPreference, which are shared preferences that encrypt keys and values. It handles AES Encryption to generate a secret key encrypted with RSA and stored in KeyStore.
For the iOS platform, it uses the KeyChain which is an iOS-specific secure storage used to store and access cryptographic keys only in your app.
In the case of the Web, it uses the Web Cryptography (Web Crypto) API.
Global State
Global state variables are pieces of information related to the device that are accessible throughout the FlutterFlow app.
These include:
- Screen size
- Platform (mobile, web, Android, iOS)
- Keyboard visibility
- Current time
These variables are found in the "Global Properties" section and are automatically added by FlutterFlow, not generated by users. Users can utilize App State variables for their own global use cases.
Global properties are retrieved through methods defined in flutter_flow_utils.dart. Typically, these methods utilize built-in Flutter libraries, such as dart:io, to gather the necessary information.
Constants
For values that do not change throughout the app, such as API keys or environment flags, we utilize the FFAppConstants class, which can be found in lib/app_constants.dart. This is an abstract class, meaning it cannot be directly instantiated. Instead, it serves as a namespace for static constants, allowing these values to be organized and accessed consistently across the application.