FlutterFlow Model
The FlutterFlowModel class is an abstract class used in FlutterFlow to provide a unified and extensible structure for managing state and behavior of widgets (both pages and components). It encapsulates initialization, state management, and disposal logic, making it easier to handle the lifecycle of widgets and their models.
FlutterFlow automatically generates the flutter_flow_model.dart file, which contains the FlutterFlowModel class and utility methods like wrapWithModel() and createModel().
The diagram below illustrates how these utility classes and methods are utilized in a widget or model class:
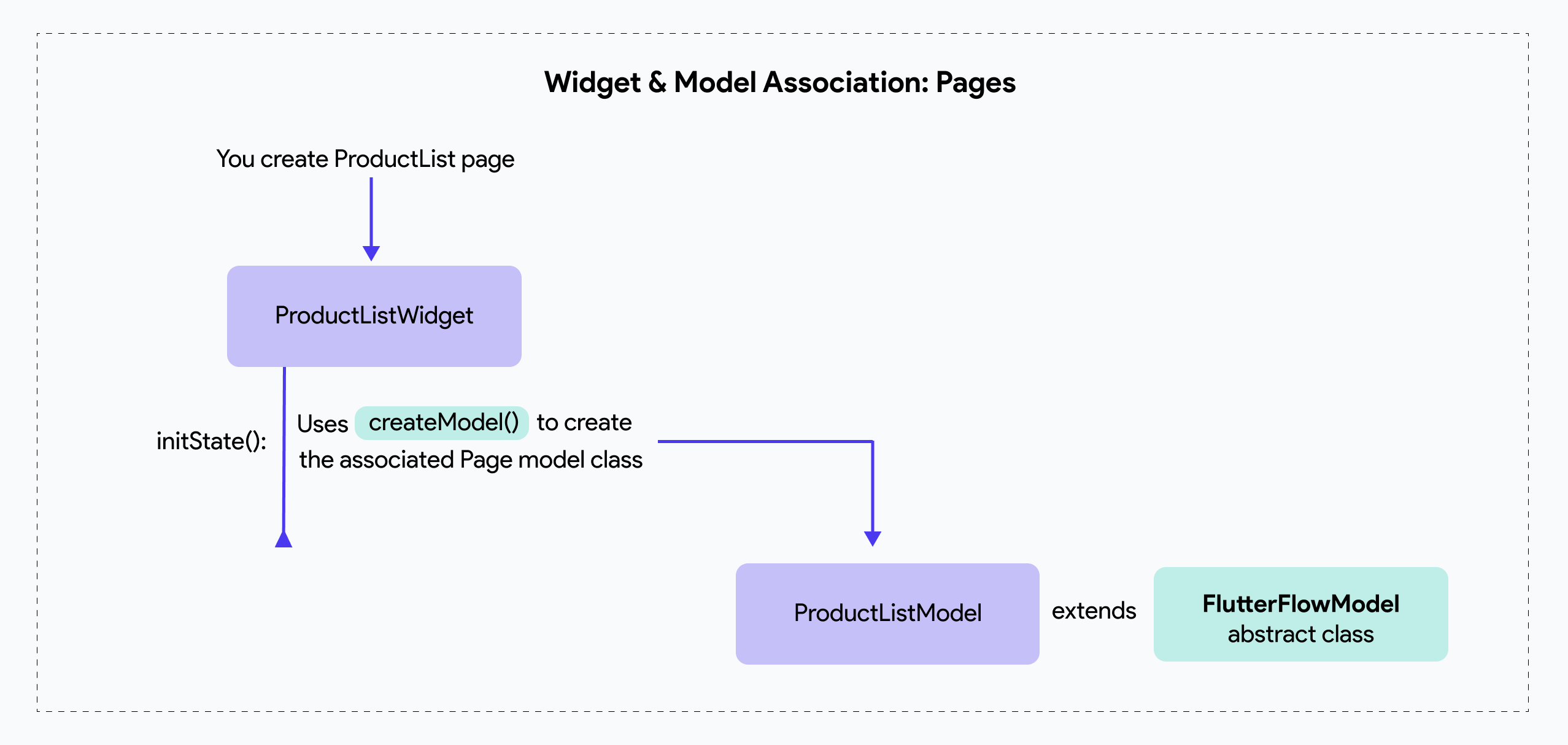
When a component is added to your page (and every component you create generates both a widget and a model class), the flow below explains how the utility classes are used when there is a child component:
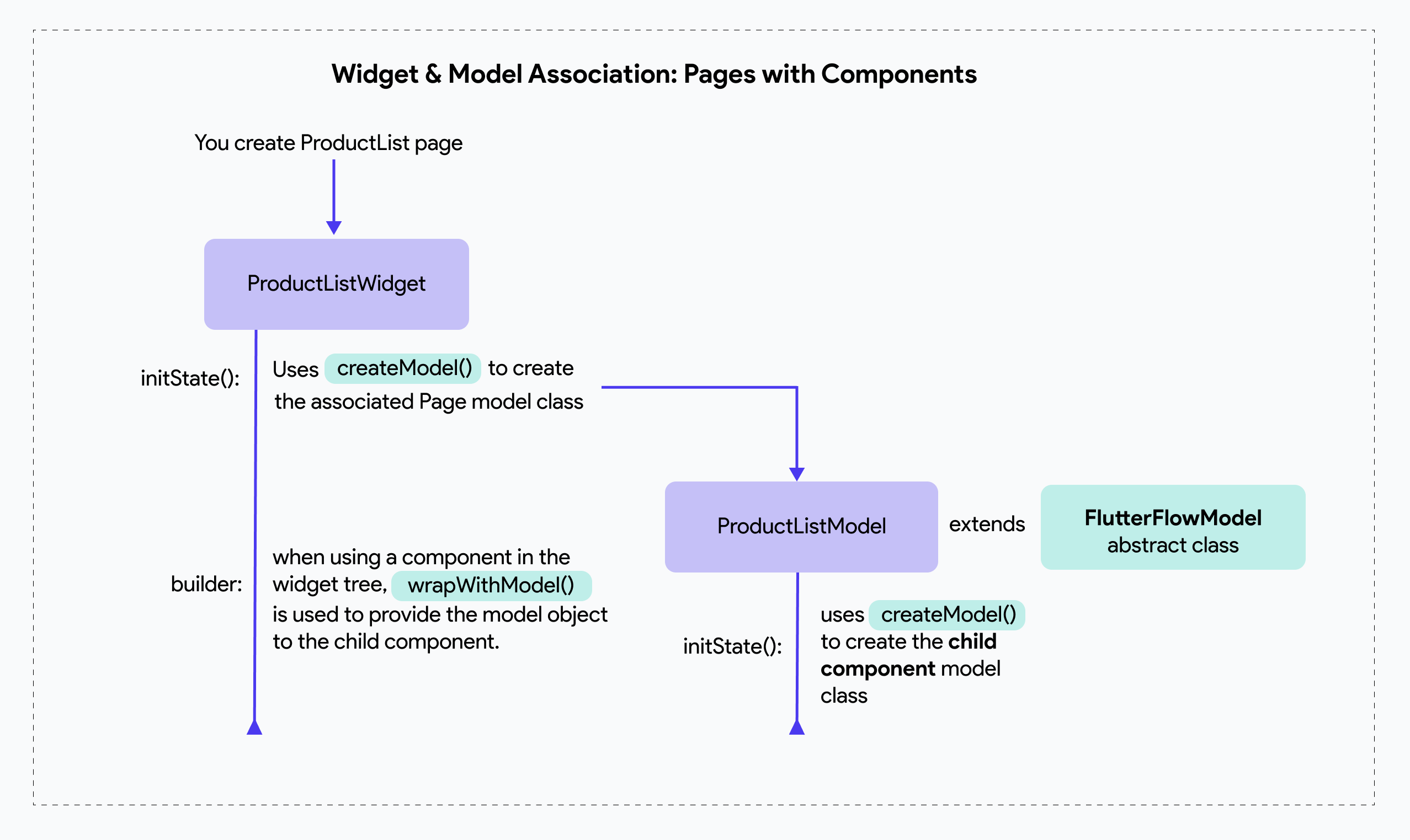
Here’s a breakdown of the lifecycle of FlutterFlowModel class:
Initialization
Ensures the model is initialized only once and is tied to the BuildContext and the widget it is associated with.
abstract class FlutterFlowModel<W extends Widget> {
// Initialization methods
bool _isInitialized = false;
void initState(BuildContext context);
void _init(BuildContext context) {
if (!_isInitialized) {
initState(context);
_isInitialized = true;
}
if (context.widget is W) _widget = context.widget as W;
_context = context;
}
Widget & Context references
Provides references to the associated widget and its BuildContext.
// The widget associated with this model. This is useful for accessing the
// parameters of the widget, for example.
W? _widget;
W? get widget => _widget;
// The context associated with this model.
BuildContext? _context;
BuildContext? get context => _context;
_widget and _context (private fields) store the widget and context references. widget and context (getters) are the public accessors for _widget and _context.
Disposal
Manages the cleanup of resources when the model or widget is disposed.
bool disposeOnWidgetDisposal = true;
void dispose();
void maybeDispose() {
if (disposeOnWidgetDisposal) {
dispose();
}
// Remove reference to widget for garbage collection purposes.
_widget = null;
}
The disposeOnWidgetDisposal determines whether the model should be disposed when the widget is removed. This defaults to true for pages and false for components (as parent models typically manage their child components).
The maybeDispose() checks disposeOnWidgetDisposal before disposing. It removes the widget reference to aid garbage collection.
Updates and Change Notification
Allows the model to notify the associated widget or parent component/page when updates occur.
// Whether to update the containing page / component on updates.
bool updateOnChange = false;
// Function to call when the model receives an update.
VoidCallback _updateCallback = () {};
void onUpdate() => updateOnChange ? _updateCallback() : () {};
FlutterFlowModel setOnUpdate({
bool updateOnChange = false,
required VoidCallback onUpdate,
}) =>
this
.._updateCallback = onUpdate
..updateOnChange = updateOnChange;
// Update the containing page when this model received an update.
void updatePage(VoidCallback callback) {
callback();
_updateCallback();
}
wrapWithModel()
The wrapWithModel() method in FlutterFlow links a model to a widget and its child widgets, allowing them to access and manage state. It wraps the widget with a Provider, making the model available throughout the widget tree.