Generated Code: Pages
When you create a new Page in FlutterFlow, it automatically generates two files: a Widget class and a Model class. So if the name of the page you created is called ProductListPage, FlutterFlow generation backend will automatically create ProductListPageWidget class and ProductListPageModel class.
This guide uses examples from the generated code of the EcommerceFlow demo app. To view the generated code directly, check out the Github repository.
PageModel class
The PageModel classes are responsible for managing the state of individual pages and initializing the components used in these Pages. These classes extend the FlutterFlowModel class, which provides a consistent structure and shared functionality across all page models.
The following diagram shows how FlutterFlow generates the model and widget class when you create a new Page in FlutterFlow:
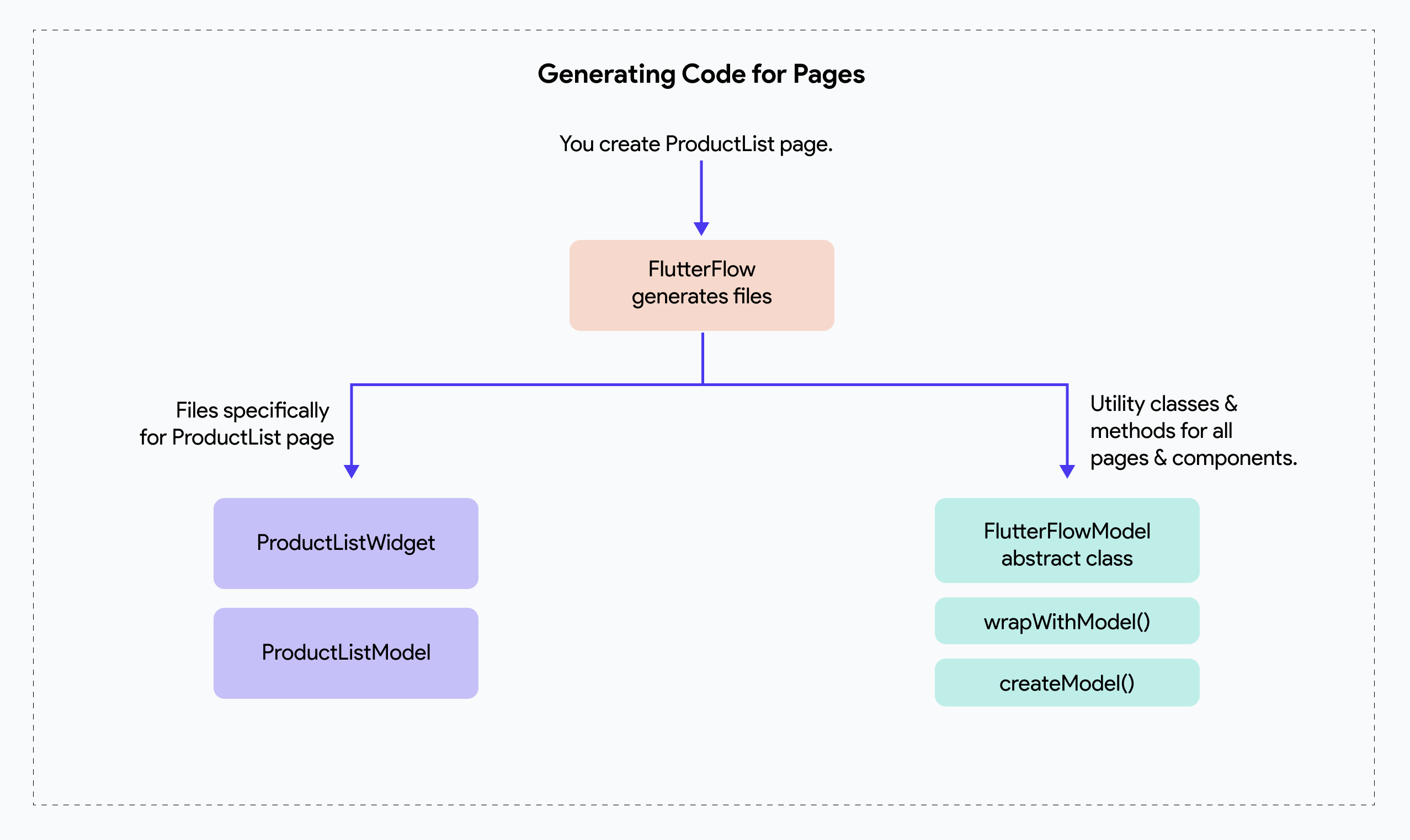
To learn more about the utility classes and methods that FlutterFlow generates for all pages & components, see the FlutterFlowModel document.
Managing Local State
A PageModel class typically holds local state fields specific to the page, which correspond to the Page State variables.
For example, in the ProductListPage, user may create a Page State variable called searchString. Correspondingly, in the product_list_page_model.dart file (which is the Model file for the ProductListPage), the corresponding state field would be _searchString. This private field stores the current search string and includes a getter and setter to manage its value while logging any changes.
String? _searchString;
set searchString(String? value) {
_searchString = value;
debugLogWidgetClass(rootModel);
}
String? get searchString => _searchString;
In Dart, variables that start with an underscore (_), such as _searchString, are private to the class. This means they cannot be accessed outside the class or its scope.
In addition to managing local state, the given PageModel class also contains fields for handling the state of widgets on the page. For instance, _dropDownValue is a private field that stores the current value of a dropdown widget (if it is added to the current Page). Similar to _searchString, it has a getter and setter that logs changes to this field.
String? _dropDownValue;
set dropDownValue(String? value) {
_dropDownValue = value;
debugLogWidgetClass(rootModel);
}
String? get dropDownValue => _dropDownValue;
Initializing child component models
The PageModel class is also responsible for initializing the models of components used on the page. For example, if the page includes a CartCounter component, the model for this component is initialized within the page's model class.
// Model for CartCounter component.
late CartCounterModel cartCounterModel;
@override
void initState(BuildContext context) {
cartCounterModel = createModel(context, () => CartCounterModel()..parentModel = this);
}
Only the model class of a child component is initialized inside the page or parent model class. In the case of page model classes, they are initialized within the widget’s state class itself. See the Widget class section for more details.
When dealing with dynamic lists of components, such as those in a ListView, Row, or Column widget, the PageModel initializes a Map<String, FlutterFlowModel> to manage the state of each component instance. For example, if the page includes a list of CategoryAvatar components, the initialization might look like this:
// Models for CategoryAvatar dynamic component.
Map<String, FlutterFlowModel> categoryAvatarModels = {};
dispose()
Finally, the dispose function in the ProductListPageModel class is used to clean up resources when they are no longer needed. This is a common practice in Flutter to prevent memory leaks. In this class, the dispose function is overridden to dispose of the cartCounterModel, searchQueryFocusNode, and searchQueryTextController.
@override
void dispose() {
cartCounterModel.dispose();
searchQueryFocusNode?.dispose();
searchQueryTextController?.dispose();
}
PageWidget class
The PageWidget classes are responsible for creating the UI of individual pages and holding the widget tree as designed in the FlutterFlow canvas. These classes always extend Flutter's StatefulWidget class utilizing Flutter's built-in state management through setState to handle dynamic updates and interact with the app's lifecycle.
class ProductListPageWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const ProductListPageWidget({super.key});
@override
State<ProductListPageWidget> createState() => _ProductListPageWidgetState();
}
PageModel Initialization
Within the State class, the PageModel object is initialized. This class serves as a centralized place to manage the page’s state, handle business logic, and interact with the data layer.
class _ProductListPageWidgetState extends State<ProductListPageWidget> {
late ProductListPageModel _model;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_model = createModel(context, () => ProductDetailPageModel());
}
PageModel Dispose
Similarly, the dispose method of the PageModel class is invoked from the overridden dispose method of the widget's State class. This ensures that any resources managed by the PageModel, such as listeners or controllers, are properly released when the widget is removed from the widget tree.
@override
void dispose() {
_model.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
Global Scaffold Key
Each page includes a GlobalKey for the Scaffold, which can be used to manage the scaffold's state, such as opening or closing drawers or snackbars programmatically.
final scaffoldKey = GlobalKey<ScaffoldState>();
return Scaffold(
key: scaffoldKey,
...)
Keyboard Dismissal
Moreover, the root widget of every page is a GestureDetector with an onTap callback that unfocuses the current input field. This approach ensures that tapping anywhere outside an input field dismisses the keyboard or removes focus, creating a better user experience.
return GestureDetector(
onTap: () {
FocusScope.of(context).unfocus();
FocusManager.instance.primaryFocus?.unfocus();
},
...)
These functionalities are automatically added by FlutterFlow to ensure seamless navigation and proper keyboard handling across pages.
onPageLoad Action: Generated Code
When you define actions for the onPageLoad action trigger of a Page, these actions are added inside an addPostFrameCallback method within the page's initState method. This ensures that the on Page Load actions are executed after the widget is fully built and rendered. This avoids issues caused by trying to update the UI before it is ready.
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_model = createModel(context, () => ProductListPageModel());
// On page load action.
SchedulerBinding.instance.addPostFrameCallback((_) async {
_model.searchString = null;
safeSetState(() {});
... // more actions
});
}
The safeSetState method is a custom implementation built on top of Flutter's setState method. It ensures that setState is only called when the widget is currently mounted, preventing potential runtime errors.