Loops
Loops in FlutterFlow allow you to perform repetitive tasks without writing complex code. This is useful when working with lists of data or when you want to repeat actions a certain number of times.
There are two types of loops supported in FlutterFlow:
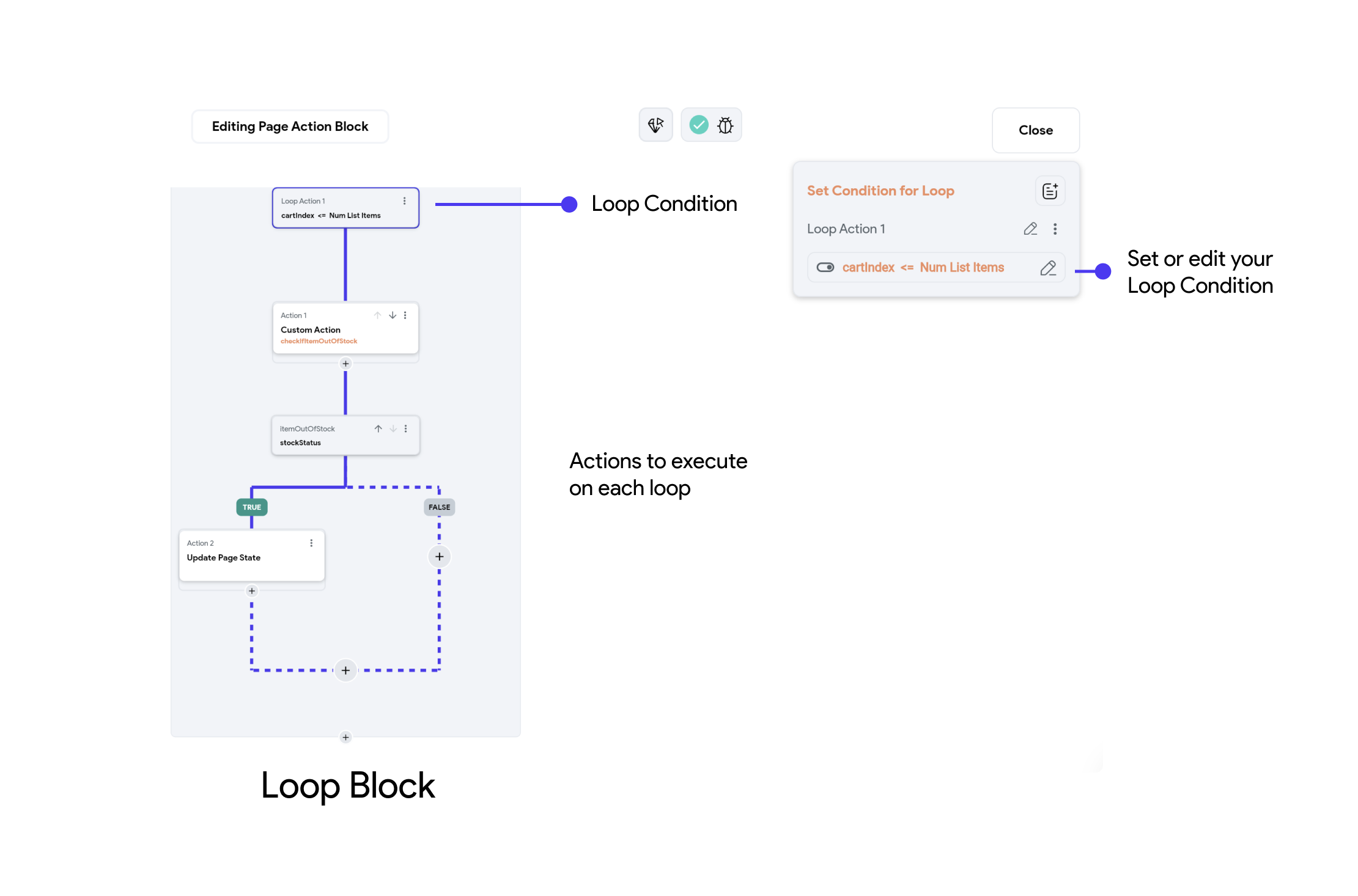
While Condition Loops
A While Condition loop requires a condition. The actions within the loop will continue to trigger as long as the condition holds true. When the condition becomes false, the loop terminates, and the next actions in the workflow will trigger.
For example, you can use a While Condition loop to continuously check if a user is still within a geofenced area. As long as the condition isUserInLocation == true holds, the app might keep checking for updates or show a live indicator.
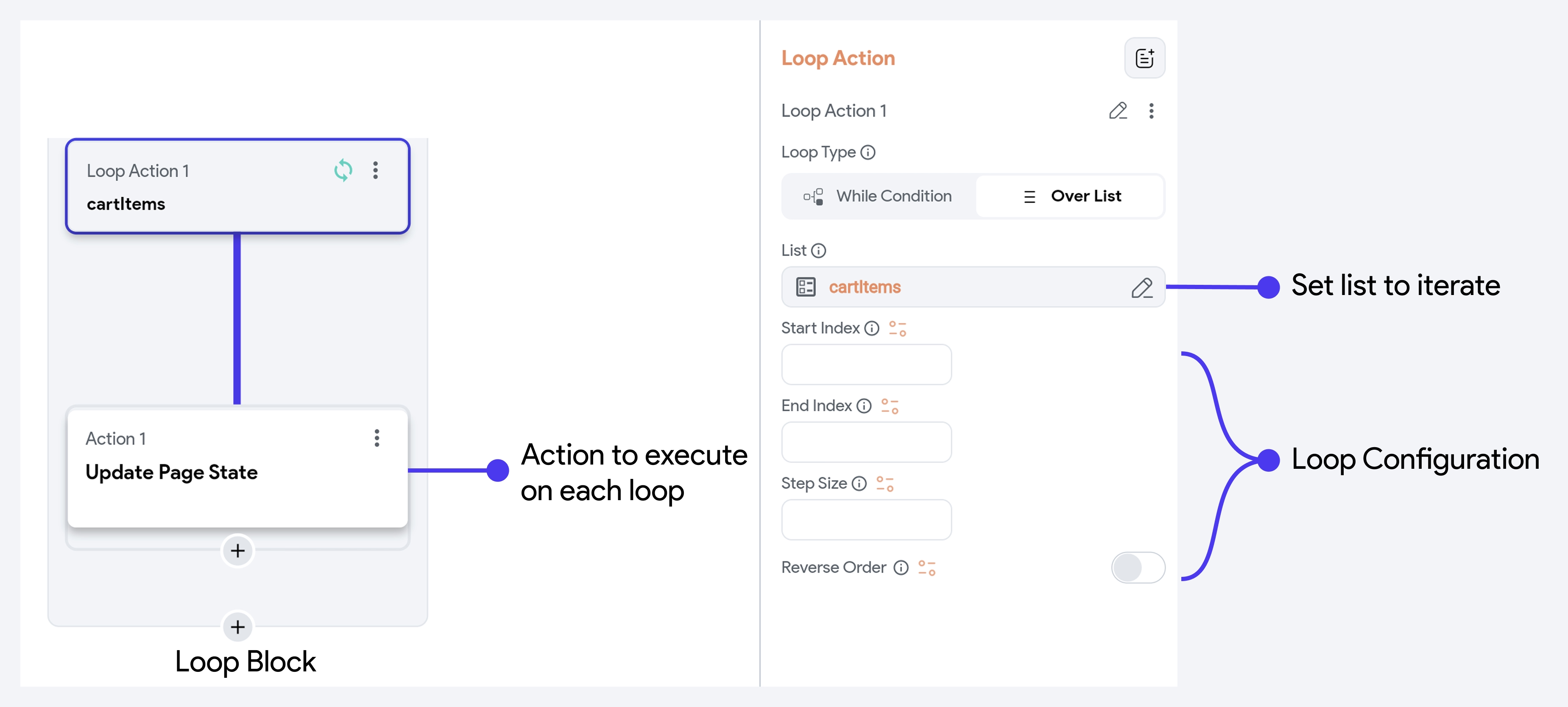
Over List
This loop type lets you iterate over a list of items to perform actions for each item in the list.
For example, if you have a list of items in a shopping cart and want to calculate the total price or apply a discount to each item, you can use Over List to go through each product and perform a calculation for each one.
You can also customize how the loop iterates:
- Start Index: Where the loop starts (default is
0). - End Index: Where the loop ends (default is the length of the list).
- Step Size: Interval between each iteration (e.g., set to
2to loop through every second item). - Reverse Order: Enables the loop to iterate from the end of the list to the beginning (e.g., showing the latest messages first).
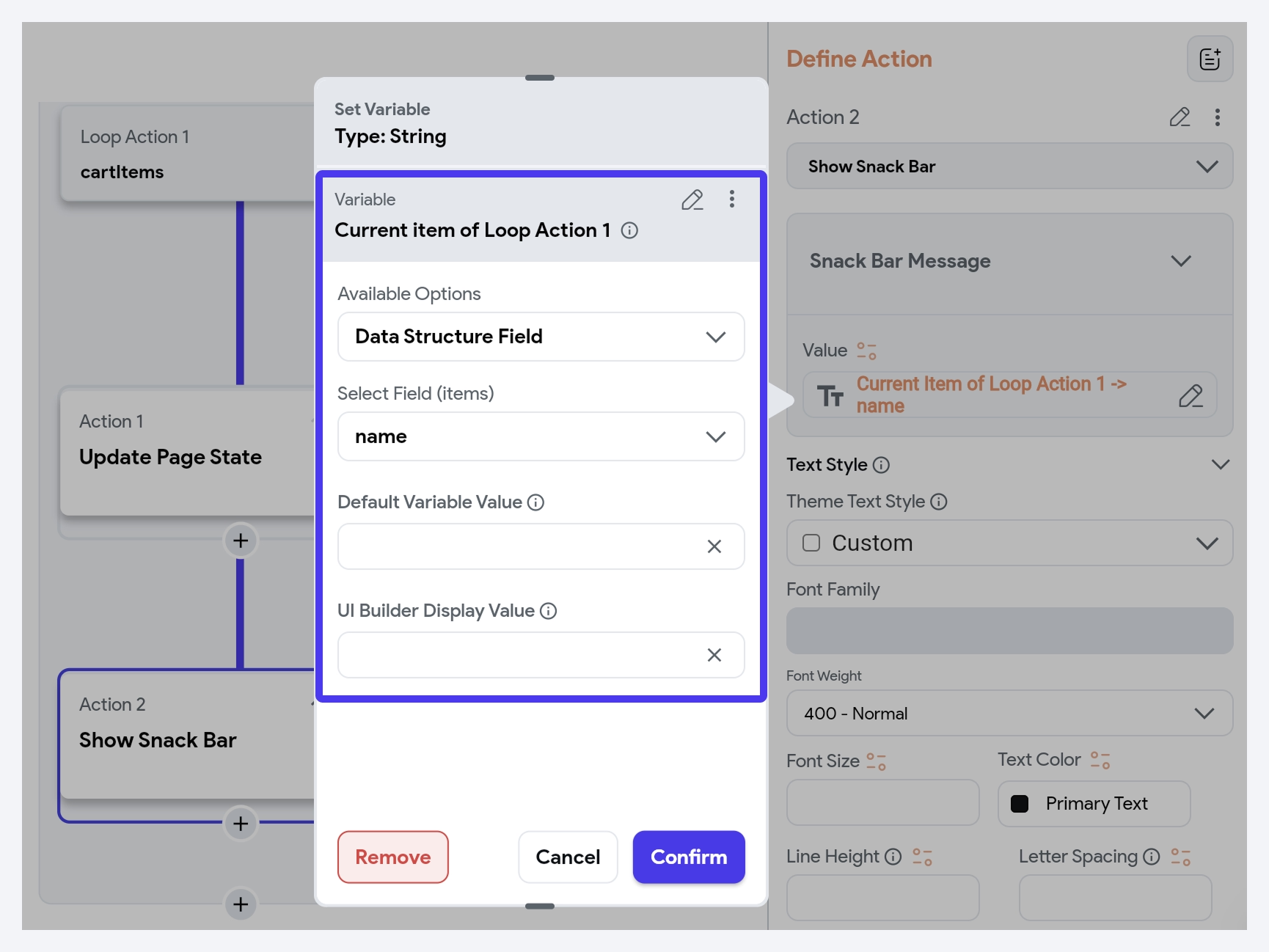
Inside a loop, you can access the current item and its index. This gives you the ability to work with each item individually, such as displaying item-specific data and making calculations.
You can also add a loop inside another loop to handle related data structures. For example, looping through orders and then looping through each order’s line items.
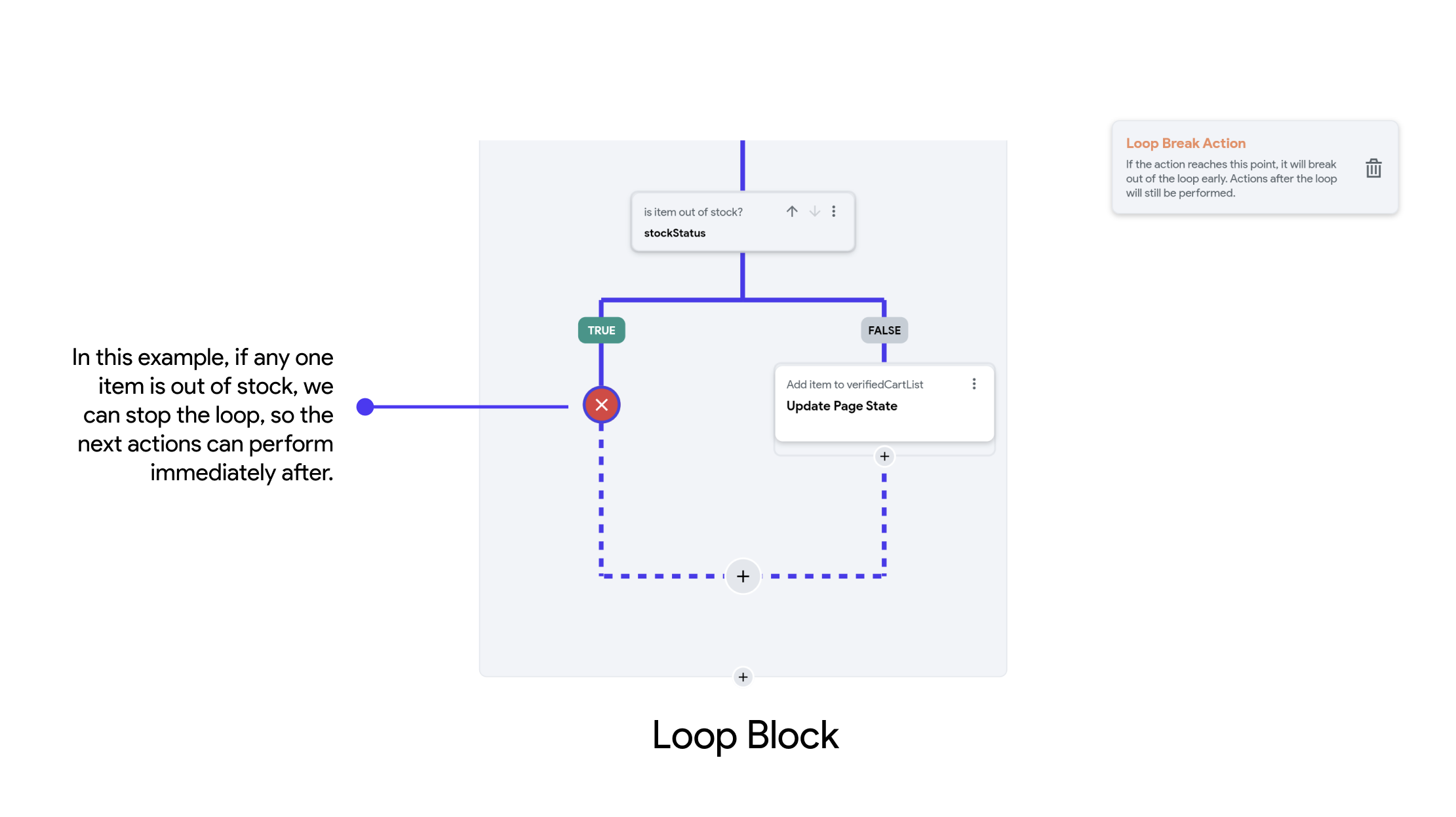
Loop Breaks
Be careful with loop actions, as they can cause your app to enter an infinite loop if the condition never becomes false. Always ensure that the condition will be met at some point so the loop can exit.
If the intended operation is completed before the condition becomes false, you must add a Loop Break action in your workflow to exit the loop.
Loop Breaks are statements used to exit a loop prematurely, before the loop's normal termination condition is met. They are typically used to stop the loop when a certain condition is satisfied, preventing unnecessary iterations and allowing the program to proceed to the next section of actions.
Key Points:
- Purpose: Exit the loop immediately when a specific condition is met.
- Implementation: Typically implemented with the "Add Break" node in Action Flow Editor.
- Usage: Commonly used to avoid infinite loops or to stop looping once a desired result is achieved.