Local Run
You can test your app on a real device using the Local Run feature, which is available in the FlutterFlow Desktop App. Local Run automatically tracks changes in your FlutterFlow project, downloads the code locally, and gives you the option to use Flutter's Hot Reload or Hot Restart to see your changes instantly on a device.
Testing on mobile devices requires downloading code, for which you must be on paid plans.
iOS Setup
For iOS app testing on a device or simulator, you need a Mac with Xcode. Follow these instructions to set up your Mac, which includes setting up your device for testing.
Android Setup
For Android app testing on a device or emulator, configure your machine (Windows, Mac, Linux) by following these instructions, which include setting up your device for testing.
Using Local Run
Here are the steps to use local run:
- Download the desktop app and open your project.
- In the Toolbar, click on the dropdown next to the Test Mode button and click Setup Local Run. This will open the setup wizard.
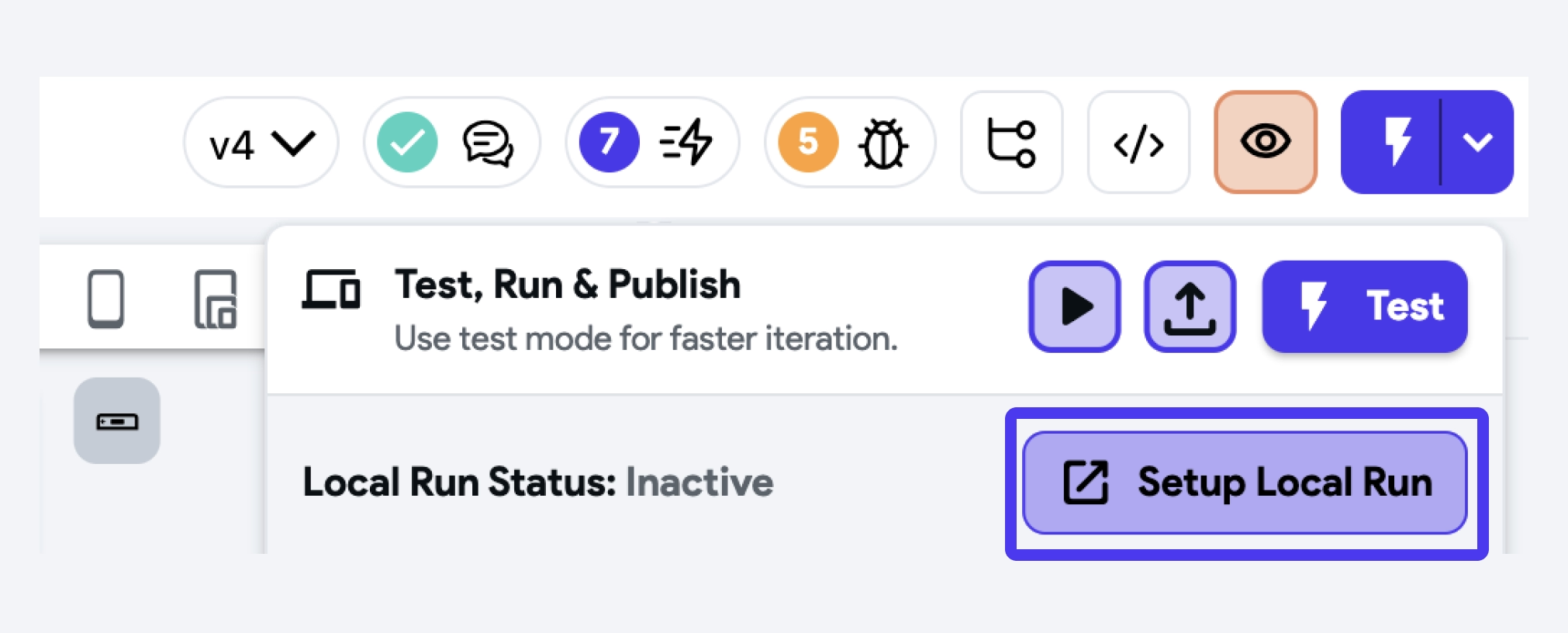
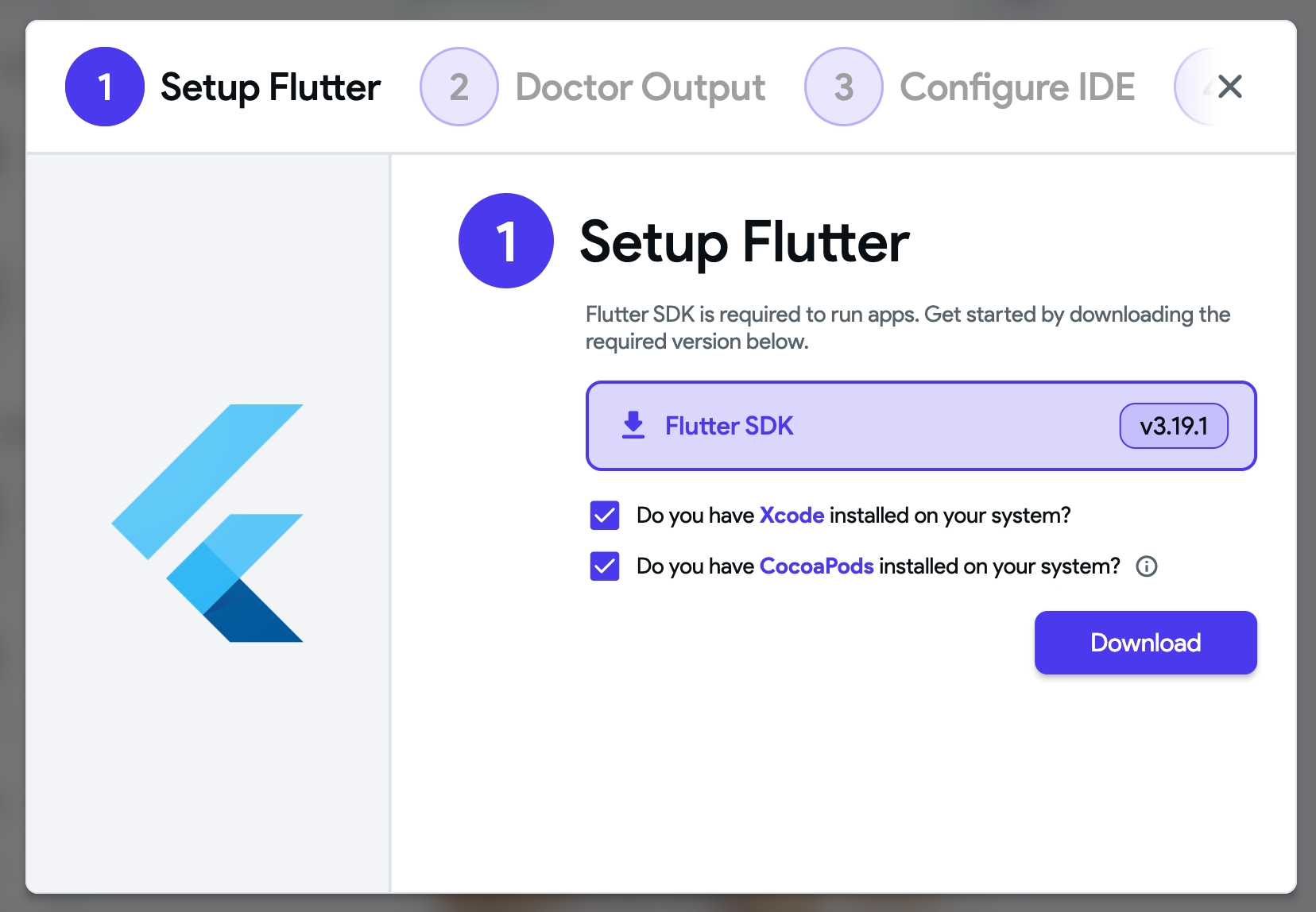
- To run the app locally, you'll need the Flutter SDK. Click the Download button to download it. Note that for iOS, ensure you have Xcode and CocoaPods installed, select the checkmark, and then click Download.
-
Once it's ready to use, click the Continue button. This will run the
Flutter Doctorcommand to check your environment for any issues that might prevent you from running the applications. It performs a series of checks to verify that the necessary tools and dependencies are correctly installed and configured on your system.
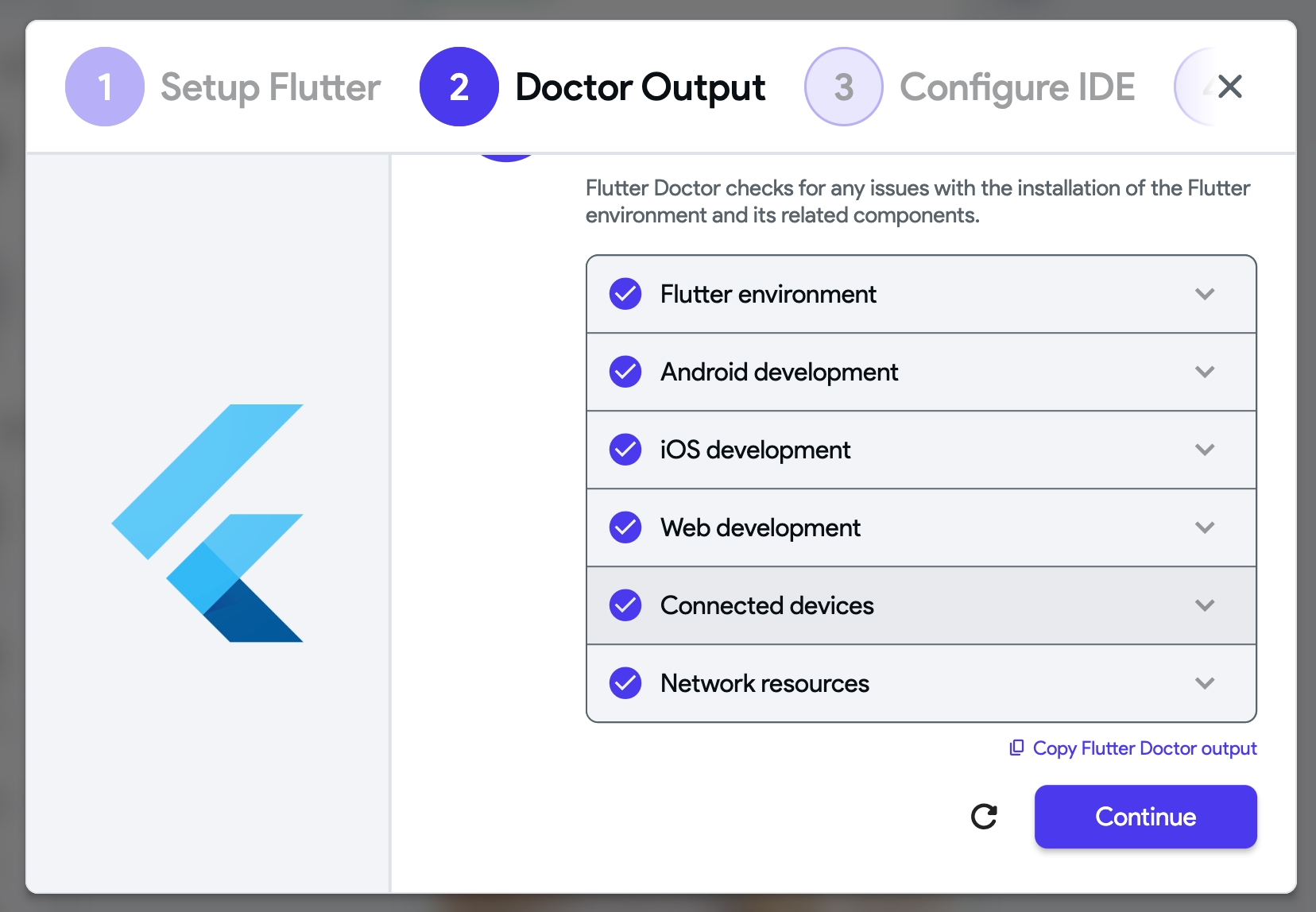
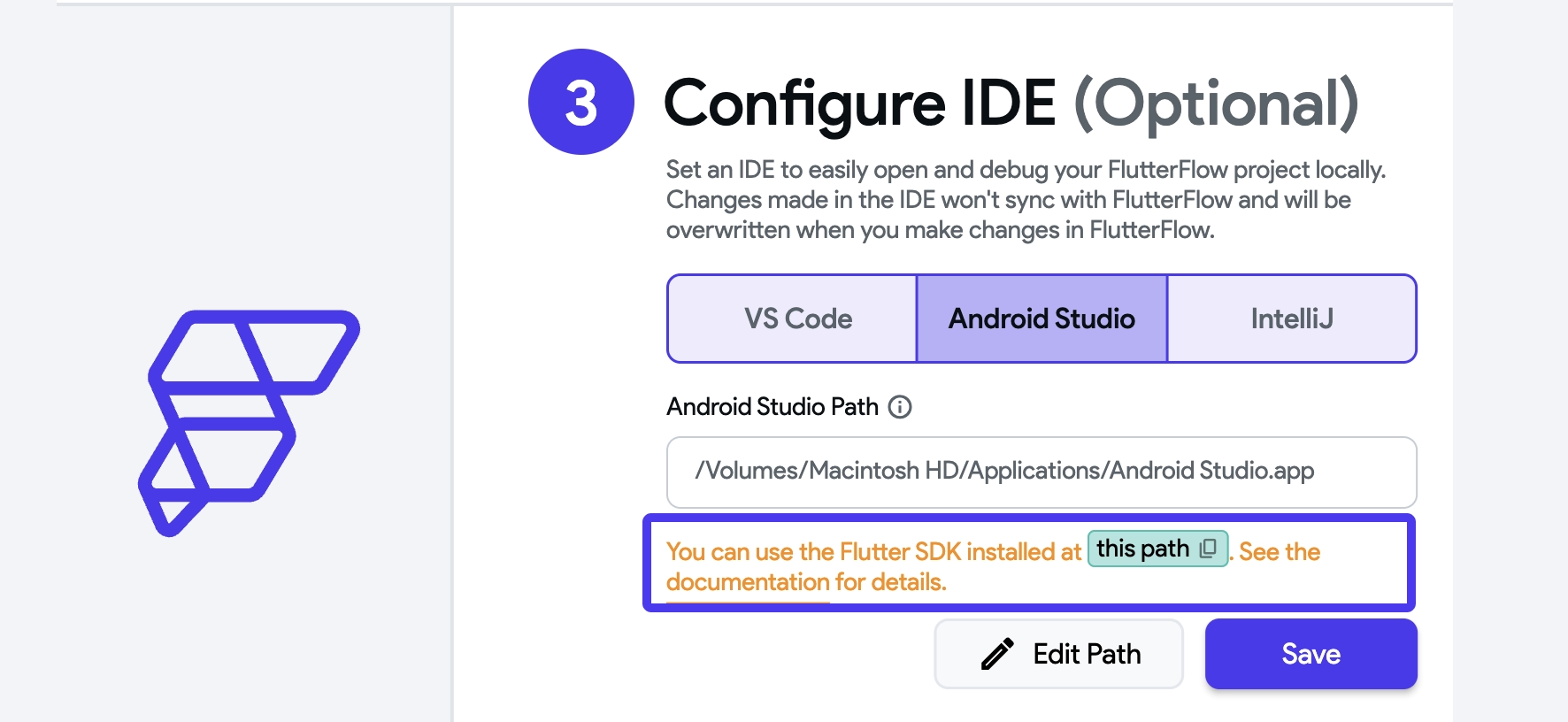
- Optional: You can set up your preferred IDE to open the project code directly from the local run. To do this, select your IDE, Select Path, and click Save. This feature is useful for debugging and understanding your project code. For this step, ensure you have setup Flutter SDK and IDE.
- The local run uses its own isolated Flutter SDK to ensure consistency and compatibility. The SDK is stored separately from any existing Flutter installations on your system and is automatically used to run your app and open projects in VS Code. For other IDEs like Android Studio, you need to set the SDK path to FlutterFlow's version manually.
- Please note that any changes made in the IDE will not sync with the FlutterFlow project and will be overwritten when you hot reload or restart the app.
- The path is the location of the IDE on your computer. On macOS, it's typically in "Applications," and on Windows, it's usually in "Program Files."
- Also, see how to access the project code.
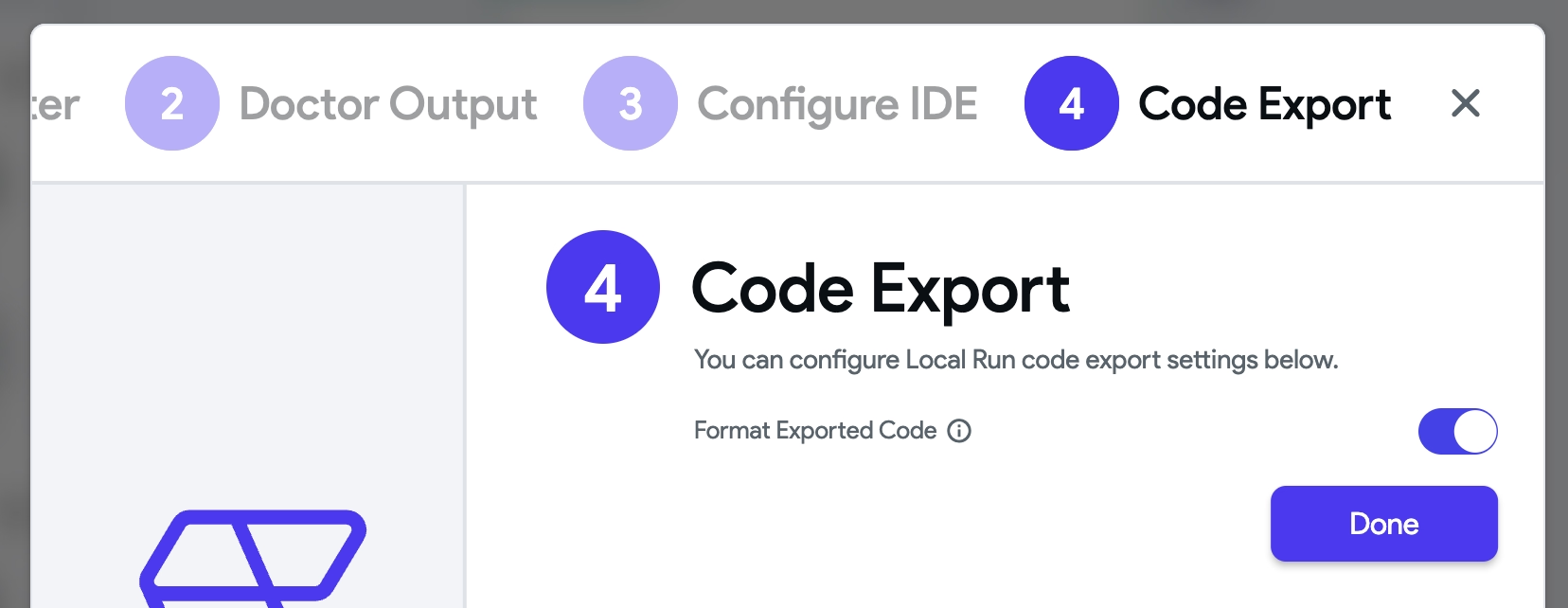
- You can also specify whether the code exported by local run should be formatted. Disabling code formatting improves the export speed which helps in faster iteration. But if you want to look into the code or make changes, it's recommended to keep this enabled.
- From the test menu, click on the Get Devices button. This will list devices connected to your system. You can add or remove devices from the list by clicking on the + and - buttons, respectively. Once you've finalized your selection, simply click on the Test button to see your app running on selected devices. Tip: In the Mac OS desktop app, you can directly open the simulator by clicking on the Launch iOS Simulator text. To test app on a real device, see how to setup a physical device.
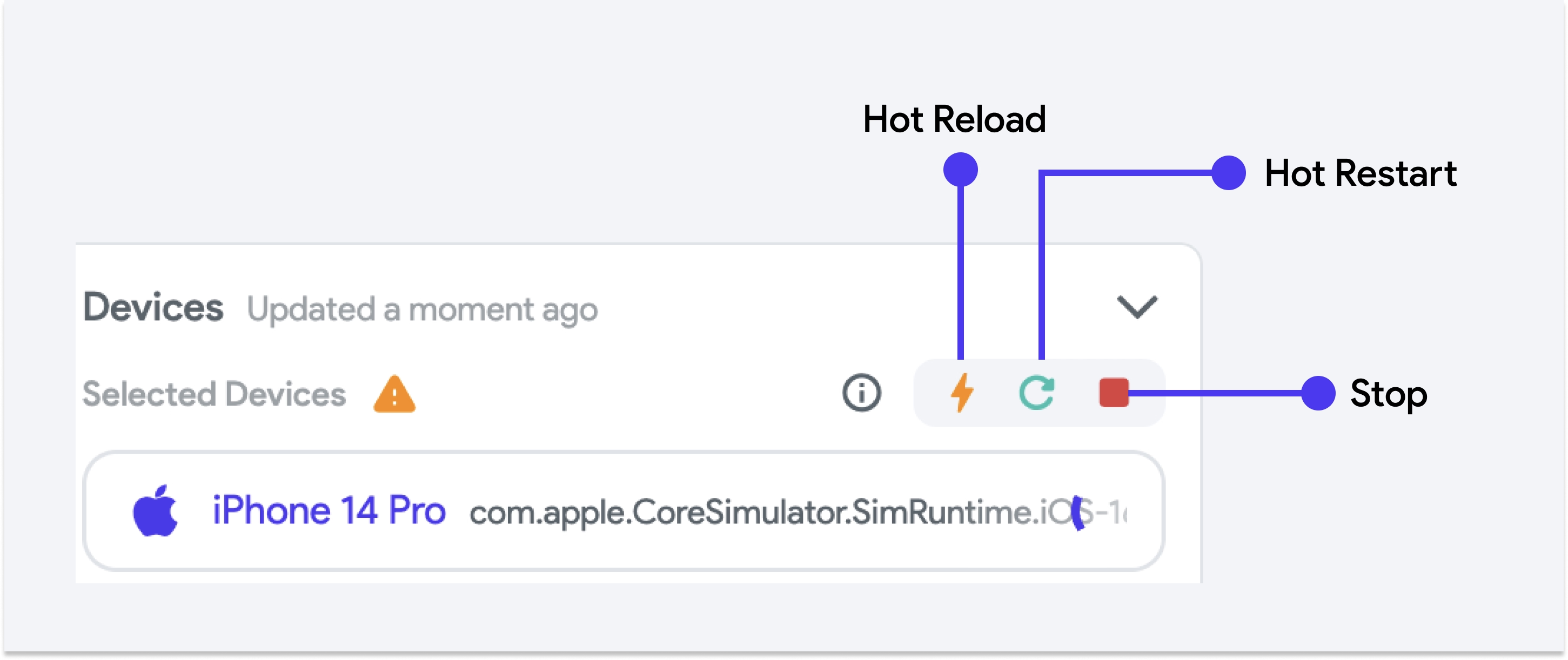
- After you make a change in your app, open the test menu to access options like hot reload, hot restart, and stopping your app. You'll notice that the test mode button has now changed to the Hot Reload button, which you can click anytime to instantly see your changes reflected on your device.
Hot Reload updates UI instantly without losing its state, while Hot Restart recompiles and reloads the entire app, resetting its state. For more info, you can visit Flutter's Hot Reload documentation.
Setup Physical Device
Testing your app on physical devices is essential to ensure it performs as expected in real-world scenarios. To set up a physical device, first, launch the project in Android Studio or Xcode, depending on the platform you are targeting. You can easily access these options by clicking on the code icon in the Local Run menu.
Setup Android Device
To setup Android physical device, first enable Developer Options and USB Debugging in your Android device. Navigate to Settings > About phone, tap Build number seven times to activate Developer Options, then go to Settings > System > Developer options and enable USB debugging.
Connect your device to your computer via USB, authorizing the connection if prompted. Verify the setup by running flutter devices in Android Studio’s terminal; your device should appear in the list of connected devices.
For more detailed guidance, refer to the Android Flutter documentation.
Setup iOS Device
To setup iOS physical device, you must configure your Apple Developer account and set up code signing in Xcode. First, add your Apple ID by opening Xcode > Preferences > Accounts, clicking "+", selecting Apple ID, and signing in.
Next, assign your project to a development team. Open your project in Xcode, select the Runner project, go to Signing & Capabilities, and choose your Apple Developer team in the Team dropdown. If your team is not listed, ensure that your Apple ID has been properly added to Xcode.
Finally, configure code signing to allow your app to run on a real device. Ensure "Automatically manage signing" is enabled. Xcode will attempt to create and download a provisioning profile for your project. If issues arise, you may need to manually create a provisioning profile in the Apple Developer Certificates, Identifiers & Profiles section. Once created, download and double-click the provisioning profile to install it in Xcode.
For more detailed guidance, refer to the iOS Flutter documentation.
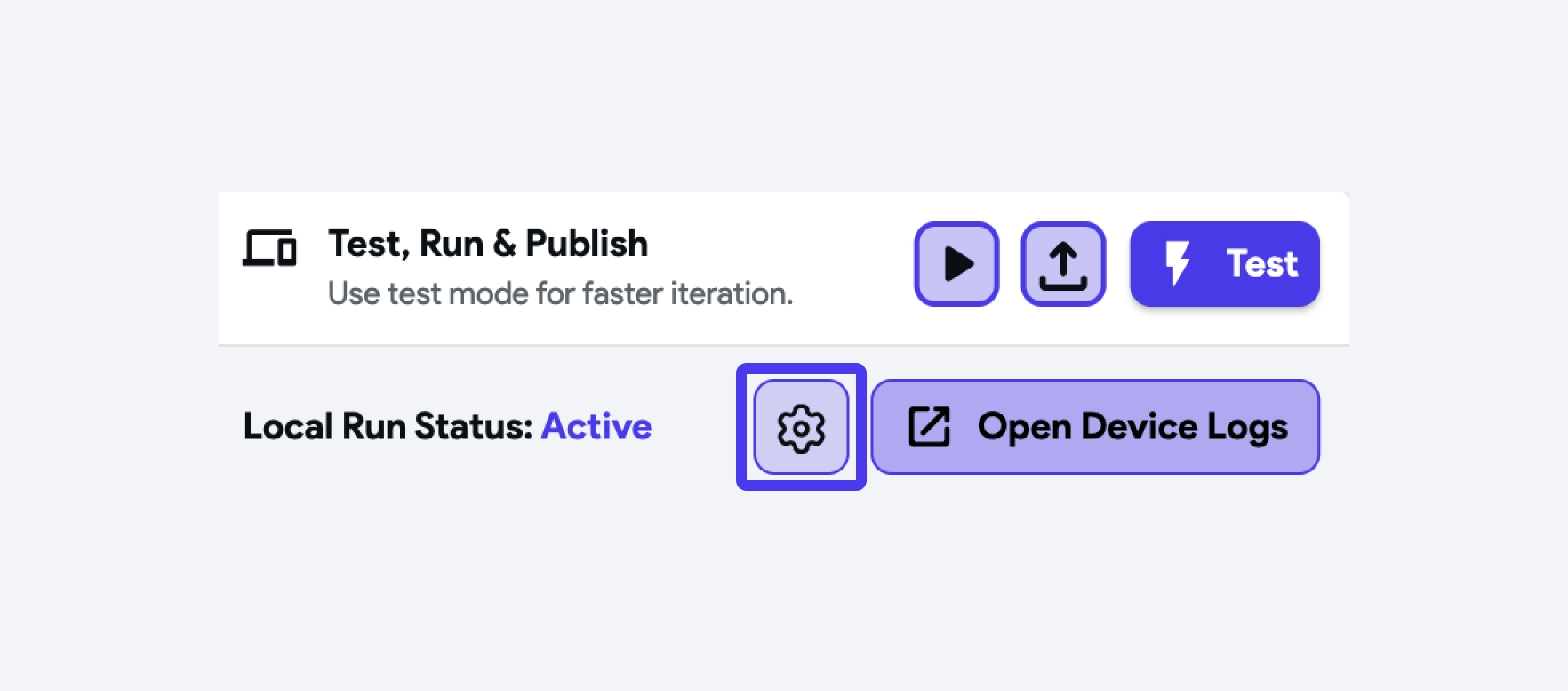
Access Device Logs in Local Run
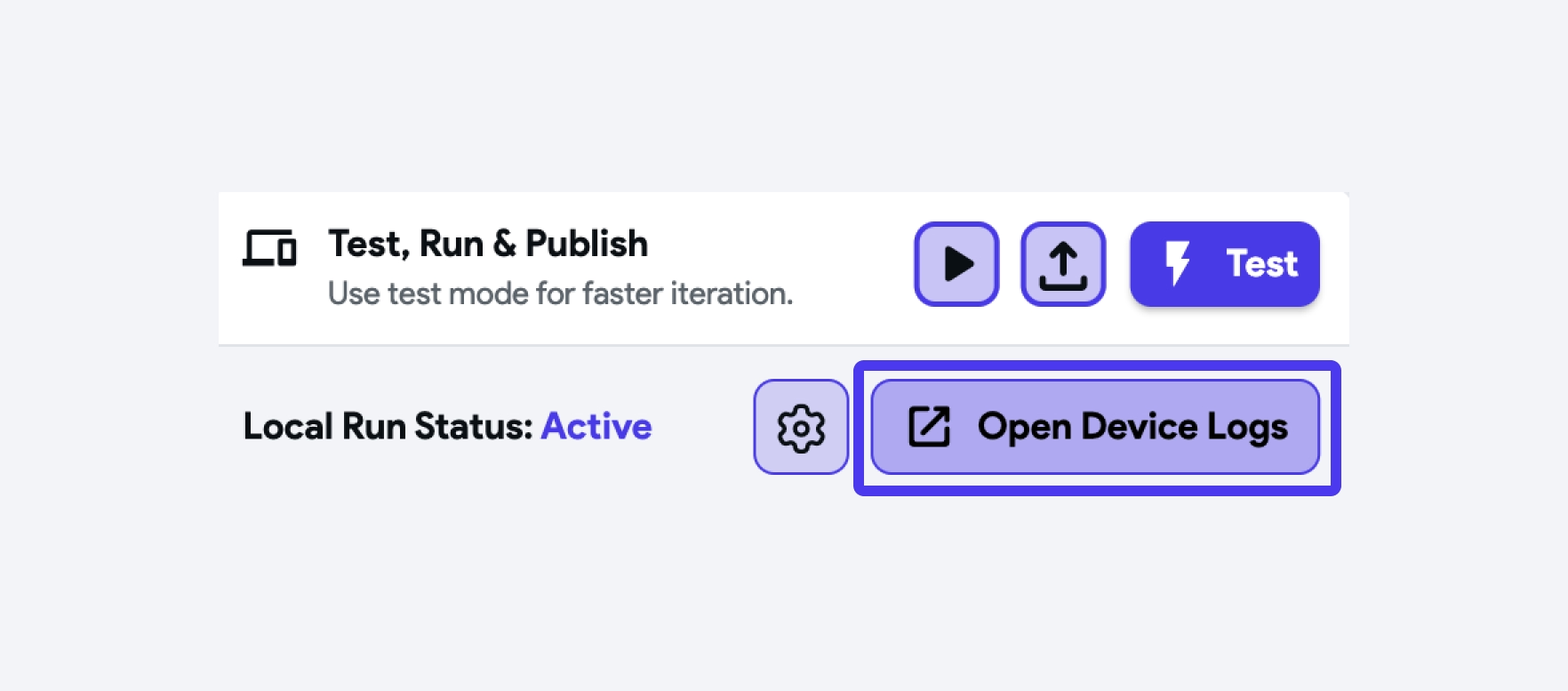
Device logs provide a way to access and view the logs generated by your app while it's running on a device or simulator. They are invaluable for understanding the inner workings of your app. If something isn't functioning as expected, the device logs can reveal the reasons behind it.
To access the device logs, first run your app using the local run. Then, open the test menu and click on Logs icon. This will display a floating window with detailed logs of the app while it's running.
Console Input
The console input in local run is particularly useful for performing hot reload and hot restart directly from the device logs. To initiate a hot reload, press r followed by Enter, and for a hot restart, press R followed by Enter. Additionally, any terminal commands commonly used with Flutter while running an app should work with the console input.
Checking Errors
Any errors displayed in the red box on your screen are also recorded in the Device logs, where you can find detailed information about the app's state and the events leading up to the issue.
Reconfigure Local Run Setup
If you need to update the Flutter SDK version, run Flutter Doctor, or start the simulator again, simply open the test menu and click Configure.
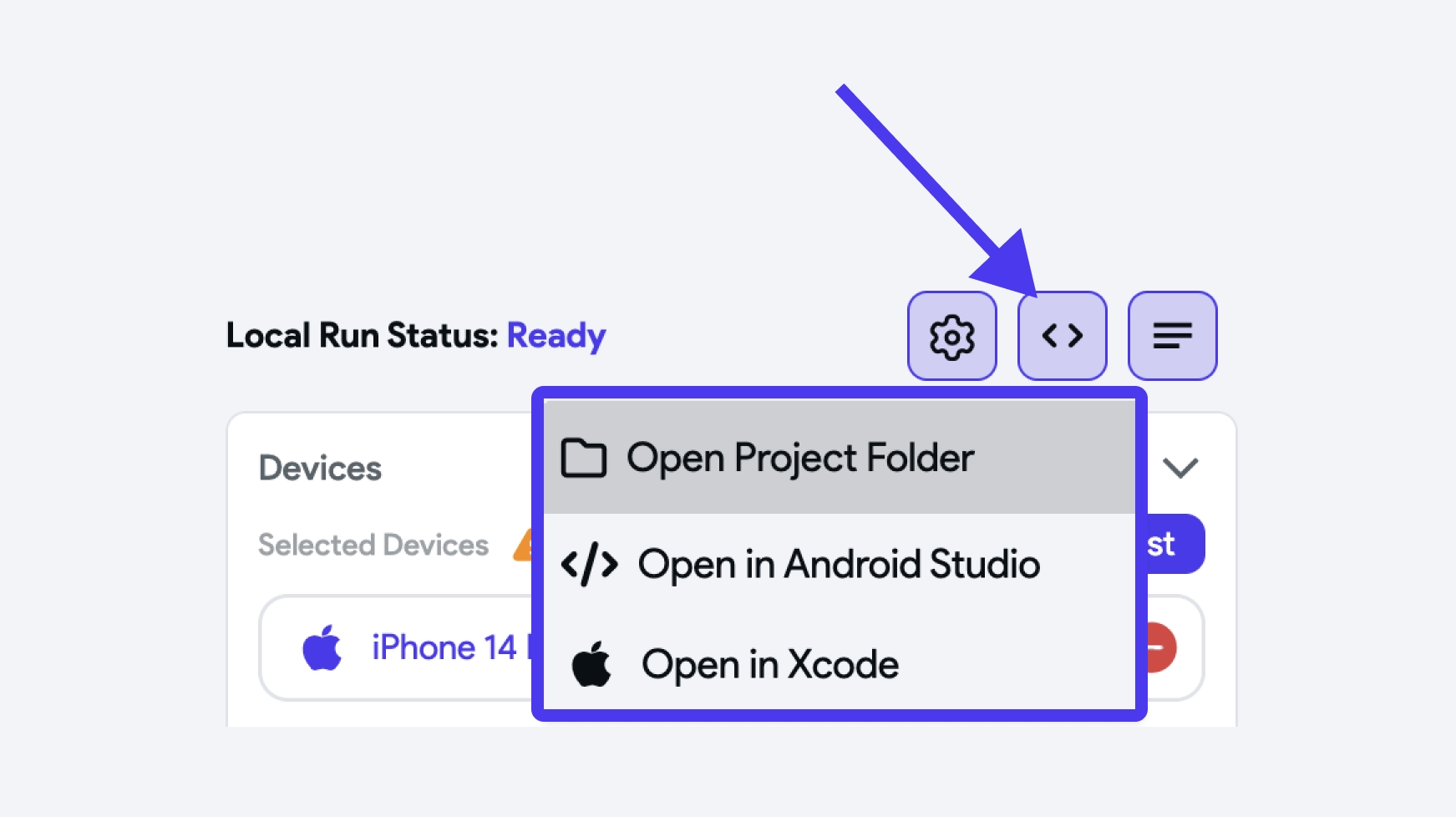
Access Project Code
To access the project code, open the test menu and ensure the project is not running. Click on the code icon, and you'll be presented with options to either open the project folder, project in your preferred IDE or directly launch the project in Xcode (for macOS users).

Manually Download Code and Run
There may be certain situations where you, as a developer, may prefer not to have local runs overwrite any changes that have been made in the code. In such cases, you can manually download the code onto your local system and then make any modifications as needed.
Here’s how you do it:
1. Download Code
- Project code download is available only on the paid plans.
- Make sure to address any project issues before downloading the code.
To download your app code, you have two options:
- Use the FlutterFlow CLI. (Recommended)
- Alternatively, from the Toolbar, click on the Developer Menu > Download Code. This will download the .zip file. Extract the .zip file to view the contents of the project.
2. Setup Flutter SDK
You can download the latest Flutter SDK from here. However, we recommend using the Flutter SDK downloaded by the local run, whether you have already downloaded the Flutter SDK or not. This approach ensures compatibility with FlutterFlow projects and helps you avoid issues arising from version differences.
To do this, copy the Flutter SDK path (click 'this path' button) from the local run and add it to your system path.
If you prefer to use your existing Flutter SDK, you can follow the steps below to avoid any versioning issues:
- Take note of your FlutterFlow project version.
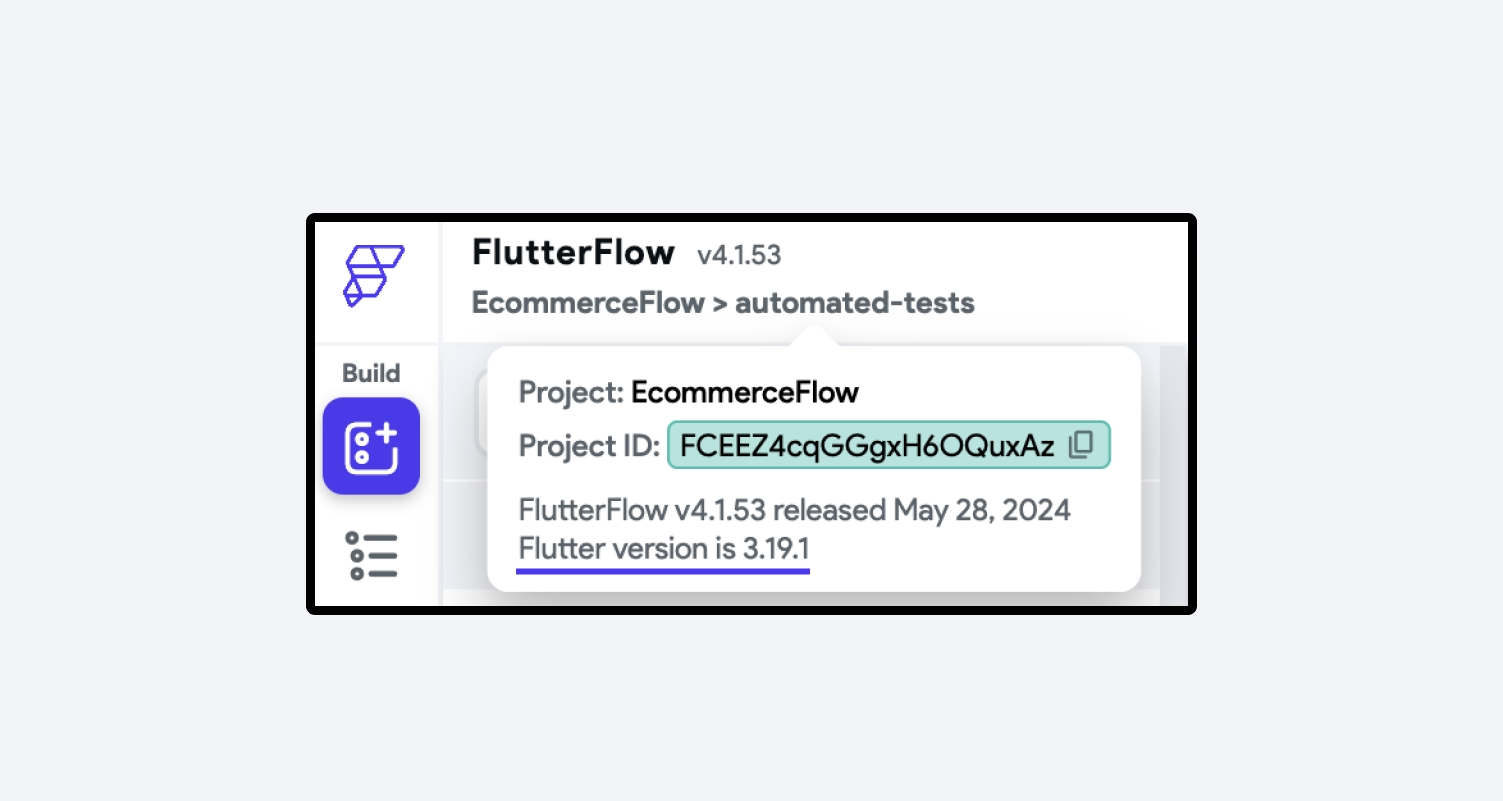
- Check your current Flutter SDK version by entering the following command in the terminal.
flutter --version - If that is different from what FlutterFlow uses, you may need to switch to the supported version.
- To install a specific version of Flutter, use the following command:
-
To downgrade flutter version:
flutter downgrade <version_number> -
To upgrade flutter version:
flutter upgrade --force <version_number>
<version_number>with the version supported by FlutterFlow. -
3. Installing IDE and Plugins
You can choose to install either Visual Studio Code or Android Studio as the IDE for your project. With either IDE, you also need the official Flutter and Dart plugins that provide you with code completion, syntax highlighting, widget editing assistance, run & debug support, and more.
- To install Visual Code with Flutter and Dart plugins, check out this link.
- To install Android Studio with Flutter and Dart plugins, check out this link.
4. Running App on Device
You can choose to run your app on a real device or an emulator.
To test app on a real device, see how to setup a physical device.
To run your app on a device:
- First open the downloaded project in your preferred IDE.
- For VS Code:
- Go to the "View" menu -> select "Terminal" from the dropdown.
- Run the command
flutter pub get. - Now, enter the command
flutter run. VS Code will build and run your app. You'll see the output in the terminal, and the app should launch in the selected emulator or physical device.
- For Android Studio:
- Open the terminal within Android Studio by clicking "View" -> "Tool Windows" -> "Terminal".
- Run the command
flutter pub get. - Click the green "Run" button (a right-facing triangle) located in the top toolbar. Choose the target device (emulator or physical device) where you want to run the app. Android Studio will build and run your app. You'll see the output in the "Run" panel at the bottom, and the app should launch in the selected emulator or device.
- If your device is not listed in the Flutter Device Selection dropdown, make sure you have properly completed the Android and iOS setup.
- If you encounter a version compatibility issue with Flutter, you can resolve it by upgrading to the latest version. Simply execute the
flutter upgradecommand in your terminal. To verify your current Flutter version, use theflutter --versioncommand.
Run on Desktop
Running your app on a Desktop involves:
- Adding platforms: Navigate to Setting and Integrations from the Navigation Menu > Project Setup > Platforms and enable your desired platform.
- Make design adjustments (optional): If you plan to target both mobile and desktop users, some design adjustments may be necessary to ensure that the UI is optimized for both platforms. You can create separate widgets for different platforms and control their visibility using Responsive Visibility.
- Run the app on a desktop: Use the Local Run feature in the FlutterFlow Desktop app or manually download and run the code, choosing your target device (e.g., macOS) before running.
Video Guide
If you prefer watching a video tutorial, here's the one for you:
Troubleshooting
Command not found: flutter (add Flutter to system's path)
If you downloaded Flutter via local run, it might not be added to your system's path. You'll need to get the Flutter SDK directory and add it to your path manually.
- For Mac
- For Windows
-
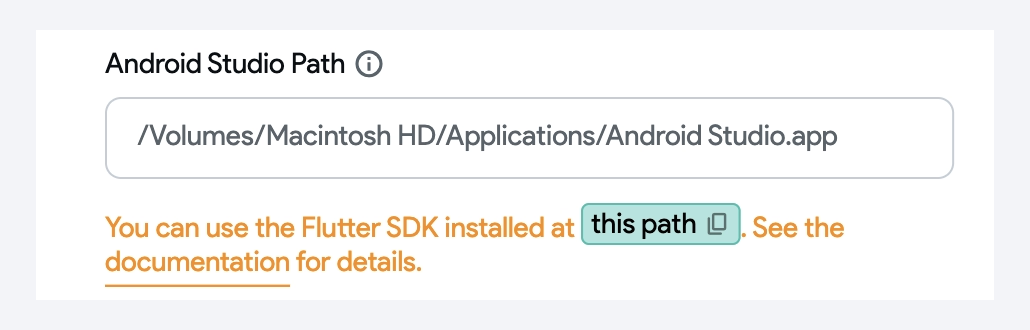
From the local run wizard, open the Configure IDE step and click on this path to get the Flutter SDK path.
-
Open the Terminal and run the following command to open your
.zshrcfile (or.bash_profileif you're using Bash):open -e ~/.zshrc -
Add path at the end of the file. It should look something like this:
export PATH="$PATH:$HOME/Library/Application Support/io.flutterflow.prod.mac/flutter/bin" -
Save and close the file.
-
Run the following command to apply the changes:
source ~/.zshrc -
Restart your terminal and try running the
fluttercommand again.
- From the local run wizard, open the Configure IDE step and click on this path to get the Flutter SDK path.

- Right-click on the Start menu and select "System".
- Click on "Advanced system settings" and then "Environment Variables".
- Under "System variables", find the "Path" variable and click "Edit".
- Click "New" and add the path to your Flutter SDK.
- Click "OK" to save your changes.
- Restart your command prompt and try running the
fluttercommand again.
Device not showing in the list
If you don't see your device in the list after refreshing, follow these steps:
-
Ensure you have added Flutter to your path.
-
Open the Terminal and run the following command:
flutter devicesThis will list all connected devices that the Local Run recognizes.
-
If you still don't see your device, try restarting it.
-
For iOS: Open Xcode, go to the "Window" menu, select "Devices and Simulators," choose your simulator, and click "Restart."
-
For Android: Open the Android Studio > Device Manager, choose your emulator, and click the "Play" button.
-
You can also restart the emulator directly from the command line using Flutter:
flutter emulators --launch <emulator_id>Note that replace
<emulator_id>with the ID of your emulator. You can find the ID by runningflutter emulators.
-
-
Try running
flutter devicesagain.
Xcode warning "Runner.xcworkspace modified"
If you encounter a warning from Xcode stating:
"The file 'Runner.xcworkspace' has been modified by another application."
This warning can usually be safely ignored. It typically occurs when multiple tools or processes (such as FlutterFlow local run and Xcode) modify the project files simultaneously. Here's what you can do:
- Save Your Work: Ensure that you've saved any changes you've made in Xcode.
- Close and Reopen: Close the warning prompt and, if necessary, close and reopen Xcode to refresh the project files.
- Clean the Build: If the warning persists, try cleaning the build folder in Xcode by going to "Product" > "Clean Build Folder."
- Flutter Clean: You can also run
flutter cleanin your terminal to clean the build cache for your project, which can sometimes resolve issues related to outdated or conflicting files.
FAQs
Can I export the project as a Flutter Module?
Yes, you can export your project as a Flutter module. Here's how:
- Activate the FlutterFlow CLI by entering
dart pub global activate flutterflow_cliin your terminal. - Use the command below to export your project and substitute
<project id>,<output folder>, and<token>with your specific project details:
flutterflow export-code --project <project id> --dest <output folder> --include-assets --token <token> --as-module
If you wish to exclude assets from the export, use --no-include-assets in your command. This will export the project code without the assets.
For example:
flutterflow export-code --project your_project_id --dest path_to_output_folder --no-include-assets --token your_token --as-module
You can then follow the instructions for Android and iOS to add the module to your main app.